Categories
- Bed Bug
- Bed Bug Cream
- BED BUG DATABASE
- Bed Bug Home Remedies
- Bed Bug Oil
- Bed Bug Remedies
- Bed Bug Spray
- Bed Bugs New York
- Bed Bugs Vancouver
- Bed Bugs World
- Bed Bugs American Samoa
- Bed Bugs Canada
- Bed Bugs Guam
- Bed Bugs North Mariana islands
- Bed Bugs Puerto Rico
- Bed Bugs United States
- Bed Bugs Alabama
- Bed Bugs Alaska
- Bed Bugs Arizona
- Bed Bugs Arkansas
- Bed Bugs California
- Bed Bugs Colorado
- Bed Bugs Connecticut
- Bed Bugs Delaware
- Bed Bugs Florida
- Bed Bugs Georgia
- Bed Bugs Hawaii
- Bed Bugs Idaho
- Bed Bugs Illinois
- Bed Bugs Indiana
- Bed Bugs Iowa
- Bed Bugs Kansas
- Bed Bugs Kentucky
- Bed Bugs Louisiana
- Bed Bugs Maine
- Bed Bugs Maryland
- Bed Bugs Massachusetts
- Bed Bugs Michigan
- Bed Bugs Minnesota
- Bed Bugs Mississippi
- Bed Bugs Missouri
- Bed Bugs Montana
- Bed Bugs Nebraska
- Bed Bugs Nevada
- Bed Bugs New Hampshire
- Bed Bugs New Jersey
- Bed Bugs New Mexico
- Bed Bugs New York
- Bed Bugs North Carolina
- Bed Bugs North Dakota
- Bed Bugs Ohio
- Bed Bugs Oklahoma
- Bed Bugs Oregon
- Bed Bugs Pennsylvania
- Bed Bugs Rhode Island
- Bed Bugs South Carolina
- Bed Bugs South Dakota
- Bed Bugs Tennessee
- Bed Bugs Texas
- Bed Bugs Utah
- Bed Bugs Vermont
- Bed Bugs Virgin Islands
- Bed Bugs Virginia
- Bed Bugs Washington
- Bed Bugs Washington DC
- Bed Bugs West Virginia
- Bed Bugs Wisconsin
- Bed Bugs Wyoming
- BedBug Removal
- BedBugs in Michigan
- Canada Bed Bugs
- Do it yourself Bed Bug
- Exterminator Bed Bugs
- Health
- Pest Inspection
- Toronto Bed Bugs
- Welcome to Bed Bugs
Registry Sites List
- Bronx Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
- Brooklyn Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
- Manhattan Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
- Nyc Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
- Queens Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
- Staten Island Bed Bug Registry Infestation Maps, Residential And Hotel
Recommended Sites
Daily Archives: November 7, 2020
News Links:
Bed bugs – Texas A&M University
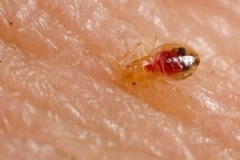
Bed bug on skin image by Pat Porter
Bed bugs are small, brownish, flattened insects that feed solely on the blood of animals. The common bed bug, Cimex lectularius, is the species most adapted to living with humans. It has done so since ancient times.
Adult bed bugs are about 1/4 inch long and reddish brown, with oval, flattened bodies. They are sometimes mistaken for ticks or cockroaches. The immatures (nymphs) resemble the adults, but are smaller and lighter in color. The youngest nymphs are approximately pinhead size and visible to the naked eye. Bed bugs do not have wings and do not fly, but can move quickly over floors, walls, ceilings and other surfaces.
Bed bug on dime, taken by Pat Porter
Bed bugs prefer to hide close to where they feed. However if necessary, they will crawl quite a ways to obtain a blood meal. Initial infestations tend to be around beds, but the bugs eventually may become scattered throughout a room, occupying any crevice or protected location. They also can spread to adjacent rooms or apartments. This can be especially problematic on college campuses, hotels and anywhere multi-housing scenarios occur. For this reason, control must be comprehensive and pest management professionals must think 3-dimensionally.
Bed bugs feed mostly at night, by piercing the skin of people as they sleep. However, if they are very hungry and if the light is dim, they will feed during the day. When bed bugs are not feeding, they spend their time in large, dense aggregations that consist of all life stages from eggs to adult. They use chemical communication to locate each other in these groups that are typically in flat, dark spaces.
When bed bugs bite, they inject a fluid into the skin that assists them in obtaining blood. Often, but not always, the fluid causes the skin to become irritated, inflamed and to itch. Elongated, spindle shaped welts can develop as a result of the bite. If the bites are on the limbs (arms or legs), these welts will be aligned with the long axis of the limb. This elongated, spindle shape can distinguish the welts from those resulting from mosquito or flea bites. In some cases, it may take several days for the reaction to occur.
If its feeding is undisturbed, a full grown bed bug becomes engorged with blood in 3 to 15 minutes. It then crawls back to its hiding place, where it remains for several days digesting its meal. When hunger returns, the bug emerges from hiding and seeks another meal of blood.
The three life stages are egg, nymph and adult.Under favorable conditions of temperature (above 70 F) and regular feeding, female bed bugs will lay about 200 eggs during their lifetime at the rate of 3 or 4 per day. Eggs are coated with a sticky substance, causing them to adhere to objects on which they are deposited. The eggs hatch in 6 to 17 days and the nymphs begin to feed on blood immediately.
After 5 molts, bed bugs reach maturity. However, bed bugs must obtain a blood meal before each molt and females must also feed before laying eggs. There may be 3 or more generations a year. Environmental factors and the availability of food will cause considerable variation in the developmental rate of all stages of growth. Young and old bed bugs may live for several weeks to several months without feeding, depending upon the temperature.
To control bed bugs in homes, locate their hiding places such as described above and treat with an insecticide approved for this use. Select a product whose label includes specific directions for bed bug control. Spray or dust beds (slats, springs and frame) and other hiding places about the room.
Because it is impossible to penetrate all hiding places, control is usually not immediate. A few living bugs may be seen for a week to 10 days after application. After 10 days, a second application, equal to the first is necessary to kill the just hatching nymphs. The pesticides used for bedbug control have a short residual life and so this second application is always needed. For heavily infested areas, it is recommended that a commercial pest control operator be consulted to control the infestation.
Always read and follow carefully the instructions on the container label.
Bed Bugs Insects in the City
Bed bugs: Do-it-yourself control options Insects in the City
Go here to see the original:
Bed bugs - Texas A&M University
Posted in Bed Bugs Texas
Comments Off on Bed bugs – Texas A&M University

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location