Click Free Pest Control Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free pest control quote today.
Printable PDF [PDF - 170 KB]
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) developed this document to highlight emerging public health issues associated with bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) in communities throughout the United States.
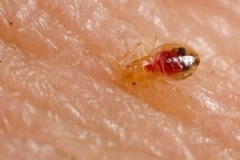
Photo 1. Bed Bug. Photo courtesy of Dr. Harold Harlan, Armed Forces Pest Management Board Image Library
Bed bugs (Photo 1) have been common in U.S. history. Although bed bug populations dropped dramatically during the mid-20th century (1), the United States is one of many countries now experiencing an alarming resurgence in the population of bed bugs. Though the exact cause is not known, experts suspect the resurgence is associated with increased resistance of bed bugs to available pesticides, greater international and domestic travel, lack of knowledge regarding control of bed bugs due to their prolonged absence, and the continuing decline or elimination of effective vector/pest control programs at state and local public health agencies.
In recent years, public health agencies across the country have been overwhelmed by complaints about bed bugs. An integrated approach to bed bug control involving federal, state, tribal and local public health professionals, together with pest management professionals, housing authorities and private citizens, will promote development and understanding of the best methods for managing and controlling bed bugs and preventing future infestations. Research, training and public education are critical to an effective strategy for reducing public health issues associated with the resurgence of bed bug populations.
Although bed bugs are not known to transmit disease, they are a pest of significant public health importance. Bed bugs fit into a category of blood-sucking ectoparasites (external parasites) similar to head lice (Pediculus humanus capitis). Bed bugs, like head lice, feed on the blood of humans but are not believed to transmit disease. Other ectoparasites, such as body lice (Pediculus humanus corporis), are known to transmit several serious diseases. Differences in the biology of similar species of pests, such as body lice and head lice (or bed bugs) can greatly impact the ability of pests to transmit disease.
Photo 2. Skin Reaction to Bed Bug bites. Photo courtesy of Dr. Harold Harlan
Bed bugs cause a variety of negative physical health, mental health and economic consequences. Many people have mild to severe allergic reaction to the bites with effects ranging from no reaction to a small bite mark to, in rare cases, anaphylaxis (severe, whole-body reaction) (2). These bites (Photo 2) can also lead to secondary infections of the skin such as impetigo, ecthyma, and lymphanigitis (3,4). Bed bugs may also affect the mental health of people living in infested homes. Reported effects include anxiety, insomnia and systemic reactions (1).
Research on the public health effects of bed bugs has been very limited over the past several decades, largely due to the noted decline in bed bug populations in the latter half of the 20th century. Now that bed bug populations are rapidly increasing, additional research is needed to determine the reasons for the resurgence, the potential for bed bugs to transmit disease and their impact on public health.
Economically, bed bug infestations are also a burden on society. Although the exact dollar amount is not known, the economic losses from health care, lost wages, lost revenue and reduced productivity can be substantial. The cost of effectively eliminating bed bugs may be significantly more than the cost of eliminating other pests because bed bug control usually requires multiple visits by a licensed pest control operator and diligence on the part of those who are experiencing the infestation. Control in multi-family homes is much more difficult than in single family homes because bed bugs frequently travel between units, either by direct transport by humans or through voids in the walls. There are additional costs and complexities associated with coordinating and encouraging participation from multiple residents.
Visit link:
CDC - EHS - Bed Bugs CDC-EPA Joint Statement
- Perfection K9 Pre-Inspections for Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: September 6th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 6th, 2011]
- Bedbug Informational Video (part two of two) [Last Updated On: September 11th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 11th, 2011]
- KDF 2010 Bed Races [Last Updated On: September 27th, 2011] [Originally Added On: September 27th, 2011]
- Raw Interview: Bedbugs, Part 3 [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2011]
- Green Lantern 5.19.10, Bedbugs [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2011]
- PPMA's Media Highlights: Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2011]
- Raw Interview: Bedbugs, Part 1 [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2011]
- Officials: Not Much Can Be Done Against Bedbugs [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2011] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2011]
- FPC Pest Control - Video [Last Updated On: November 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: November 8th, 2011]
- Dr. Michael Potter Talks About Bed bugs and ESA - Video [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 3rd, 2011]
- Bed Bug Feeding - Time Lapsed Best Quality HD - Video [Last Updated On: December 8th, 2011] [Originally Added On: December 8th, 2011]
- Unwelcome guests drive Henry Tower residents buggy [Last Updated On: February 14th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 14th, 2012]
- Top Entomologists Call 2012 Pivotal Year in Bed Bug War [Last Updated On: February 29th, 2012] [Originally Added On: February 29th, 2012]
- Combating bed bugs for the World Choir Games [Last Updated On: May 19th, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 19th, 2012]
- Bed bugs a problem in homes, not city offices [Last Updated On: May 23rd, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 23rd, 2012]
- All Natural Bed Bug Solution Driven by Consumer Demand and Science [Last Updated On: May 23rd, 2012] [Originally Added On: May 23rd, 2012]
- Bed bugs: How not to bring them home from summer vacation hot spots [Last Updated On: June 15th, 2012] [Originally Added On: June 15th, 2012]
- Kentucky: Cabinet for Health and Family Services - Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Natural Remedy for Bed Bugs | eHow - eHow | How to Videos ... [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2013]
- Bed Bugs | Public Health and Medical Entomology | Purdue ... [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2013]
- Bed Bugs – ThermaPure [Last Updated On: December 19th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 19th, 2013]
- Natural Bed Bug Spray EcoRaider Garnered Attention at Global Bed Bug Summit [Last Updated On: December 20th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 20th, 2013]
- Building A Better Bed Bug Trap | Popular Science [Last Updated On: December 21st, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 21st, 2013]
- Scherzinger - Bed Bugs | Bed Bugs Services | OH | KY ... [Last Updated On: December 23rd, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 23rd, 2013]
- Reports of Bed Bugs in Louisville Hotels - Louisville ... [Last Updated On: December 28th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 28th, 2013]
- Get Rid of BedBugs in Lexington, KY - Call Innovative Pest ... [Last Updated On: January 20th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 20th, 2014]
- Bedbug education and safety a concern [Last Updated On: February 12th, 2014] [Originally Added On: February 12th, 2014]
- Bedbugs: An Unwanted Souvenir [Last Updated On: March 19th, 2014] [Originally Added On: March 19th, 2014]
- ANCHORAGE, Alaska: Complaints of bedbugs increase in ... [Last Updated On: March 20th, 2014] [Originally Added On: March 20th, 2014]
- Tips for Staying Bed Bug Free This Travel Season [Last Updated On: April 17th, 2014] [Originally Added On: April 17th, 2014]
- IN Bed Bug Control Gets Rid Of Bed Bugs In Indiana ... [Last Updated On: April 19th, 2014] [Originally Added On: April 19th, 2014]
- KILL BED BUGS IN FLORENCE | 513-546-1224 | 41042 | KILL ... [Last Updated On: May 7th, 2014] [Originally Added On: May 7th, 2014]
- Bed bug cases growing across the Tri-State - 14 News, WFIE ... [Last Updated On: July 10th, 2014] [Originally Added On: July 10th, 2014]
- The latest weapon in the battle against bedbugsluggage [Last Updated On: October 8th, 2014] [Originally Added On: October 8th, 2014]
- The National Pest Management Association Reminds Thanksgiving Travelers to Pack Bed Bug Prevention Tips [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2014] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2014]
- Kentucky.gov: - Bed Bugs 07 [Last Updated On: January 4th, 2015] [Originally Added On: January 4th, 2015]
- That bites! BG among worst bedbug cities [Last Updated On: January 27th, 2015] [Originally Added On: January 27th, 2015]
- bed bug - Cimex lectularius Linnaeus - University of Florida [Last Updated On: August 9th, 2015] [Originally Added On: August 9th, 2015]
- Bed Bugs Forum [Last Updated On: October 7th, 2015] [Originally Added On: October 7th, 2015]
- UK Research: Bed Bugs 'Bite' the Wallet of Hotel Owners ... [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Northern Kentucky Health Department | Bed Bugs at Work [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Bed Bug Resources | Entomological Society of America (ESA) [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs | Pest Control | Louisville, KY | IPM Services [Last Updated On: March 7th, 2016] [Originally Added On: March 7th, 2016]
- Northern Kentucky Health Department | Bed Bug Fact Sheet [Last Updated On: April 9th, 2016] [Originally Added On: April 9th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs: Everyone is vulnerable - WDRB 41 Louisville News [Last Updated On: May 5th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 5th, 2016]
- How Does a Person Get Bed Bugs? | eHow [Last Updated On: May 16th, 2016] [Originally Added On: May 16th, 2016]
- Bed Bugs, BedBugs, Survery, 2011 Bugs Without Borders ... [Last Updated On: January 2nd, 2017] [Originally Added On: January 2nd, 2017]
- Know Where Bed Bugs Hide - BadBedBugs.com [Last Updated On: January 8th, 2017] [Originally Added On: January 8th, 2017]
- Hartshorne City Hall closed after discovery of bedbugs - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: February 15th, 2017] [Originally Added On: February 15th, 2017]
- DC elementary school reopens after bed bugs, rodents found - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: February 28th, 2017] [Originally Added On: February 28th, 2017]
- Bedbugs force 3 South Carolina fire crews to relocate | Lexington ... - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: June 5th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 5th, 2017]
- Avoid the Biting Burden of Bed Bugs This Summer - satPRnews (press release) [Last Updated On: June 5th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 5th, 2017]
- Angry man releases about 100 bed bugs at Maine city office - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: June 6th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 6th, 2017]
- Most consumers can't identify bed bugs, survey finds - ConsumerAffairs [Last Updated On: June 14th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 14th, 2017]
- Do you know how to spot a bedbug? - CBS News - CBS News [Last Updated On: June 14th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 14th, 2017]
- Bed Bug Awareness is Poor Among US Travelers, But Reactions are Strong - Infection Control Today [Last Updated On: June 14th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 14th, 2017]
- Survey: Bed Bugs Are the Last Thing Travelers Want to See in a ... - Entomology Today [Last Updated On: June 15th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 15th, 2017]
- Could You Spot Bed Bugs in a Hotel Room? - WebMD - WebMD [Last Updated On: June 15th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 15th, 2017]
- Travelers are terrified by bed bugs -- but can't spot one in a lineup - AOL [Last Updated On: June 16th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 16th, 2017]
- Bed bug awareness poor among US travelers, but reactions are strong - Phys.Org [Last Updated On: June 19th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 19th, 2017]
- Bed bug scare looms large for hotel, lodging industry - Daily News & Analysis [Last Updated On: June 20th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 20th, 2017]
- Bed Bugs Are Back: What You Need To Know - WCNC [Last Updated On: June 23rd, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 23rd, 2017]
- Spiders, Snakes, Bedbugs and No Bathroom Privacy Oh My! - ChicagoNow (blog) [Last Updated On: June 23rd, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 23rd, 2017]
- Bed Bugs Are Back: What You Need To Know - WFMY News 2 [Last Updated On: June 24th, 2017] [Originally Added On: June 24th, 2017]
- Man who threw bedbugs at Maine municipal office is charged - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: July 7th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 7th, 2017]
- Surprising Places Bed Bugs Can Hide - ConsumerReports.org [Last Updated On: July 13th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 13th, 2017]
- Central Illinois struggles to find solution for bed bugs - Lexington Herald Leader [Last Updated On: July 25th, 2017] [Originally Added On: July 25th, 2017]
- How to Check for Bed Bugs: Detection Tips - Orkin.com [Last Updated On: November 22nd, 2017] [Originally Added On: November 22nd, 2017]
- Bed Bugs - Pest Control Tips from Exterminators [Last Updated On: January 29th, 2018] [Originally Added On: January 29th, 2018]
- BED BUGS | Ace Kentucky [Last Updated On: September 11th, 2018] [Originally Added On: September 11th, 2018]
- Kentucky, United States Bed Bug Registry Map Bed Bug ... [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2018] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2018]
- Bed Bug News Reports Bed Bugs in Kentucky [Last Updated On: December 7th, 2018] [Originally Added On: December 7th, 2018]
- Bed Bug Biology and Behavior - UNIVERSITY OF KENTUCKY [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2019] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2019]
- Bed Bugs - Cabinet for Health and Family Services [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2019] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2019]
- Bed bug sniffing dogs could be the best defense against infestation - 10TV [Last Updated On: February 23rd, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 23rd, 2020]
- Bed Bugs and Schools | Managing Pests in Schools | US EPA [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2020]
- Kentucky Bed Bug Hotel and Apartment Reports ... [Last Updated On: March 18th, 2020] [Originally Added On: March 18th, 2020]
- Bed Bugs Modify Microbiome of Homes They Infest - NC State News [Last Updated On: July 15th, 2020] [Originally Added On: July 15th, 2020]
- Bed Bugs - University of Kentucky [Last Updated On: July 28th, 2020] [Originally Added On: July 28th, 2020]
- Two KY Cities Pop Up on a National 'Most Bed Bugs' ListGood ... - WBKR [Last Updated On: October 16th, 2023] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2023]
Click Free Exterminator Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free exterminator quote today.