WHAT ARE BED BUGS?
Bed bugs are small insects that feed on human blood. They are usually active at night when people are sleeping. Adult bed bugs have flat rusty-red-colored oval bodies. Adult bed bugs are about the size of an apple seed, they are big enough to be easily seen, but often hide in cracks in furniture, floors, or walls. When bed bugs feed, their bodies swell and become brighter red. They can live for several months without feeding on a host.
WHAT DOES A BED BUG BITE FEEL AND LOOK LIKE?
Most bed bug bites are initially painless, but later turn into large, itchy skin welts. These welts do not have a red spot in the center as do the bites from fleas.
ARE BED BUGS DANGEROUS?
Although bed bugs and their bites are a nuisance, they are not known to spread diseases.
HOW DOES A HOME BECOME INFESTED WITH BED BUGS?
In most cases, people carry bed bugs into their homes unknowingly, in infested luggage, furniture, bedding, or clothing. Bed bugs may also travel between apartments through small crevices and cracks in walls and floors.
HOW DO I KNOW IF MY HOME IS INFESTED WITH BED BUGS?
You may notice itchy skin welts. You may also see the bed bugs themselves, small bloodstains from crushed insects, or dark spots from their droppings. It is often hard to find them because they hide in or near beds, other furniture, and in cracks.
SHOULD I USE A PEST CONTROL COMPANY?
The Health Department recommends that homeowners hire pest control companies registered by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) to get rid of bed bugs.
| State of New York | |||||
|
|||||
| Nickname(s): The Empire State | |||||
| Motto(s): Excelsior (Latin)[1]Ever upward | |||||
 |
|||||
| Official language(s) | English | ||||
| Demonym | New Yorker | ||||
| Capital | Albany | ||||
| Largest city | New York City | ||||
| Largest metro area | New York City Metropolitan Area | ||||
| Area | Ranked 27th in the U.S. | ||||
| – Total | 54,556[2] sq mi(141,300 km2) | ||||
| – Width | 285 miles (455 km) | ||||
| – Length | 330 miles (530 km) | ||||
| – % water | 13.5 | ||||
| – Latitude | 40° 30′ N to 45° 1′ N | ||||
| – Longitude | 71° 51′ W to 79° 46′ W | ||||
| Population | Ranked 3rd in the U.S. | ||||
| – Total | 19,378,102 (2010 Census)[3] | ||||
| – Density | 408.7/sq mi (157.81/km2)Ranked 7th in the U.S. | ||||
| Elevation | |||||
| – Highest point | Mount Marcy[4][5][6]5,343 ft (1628.57 m) | ||||
| – Mean | 1,000 ft (300 m) | ||||
| – Lowest point | Atlantic Ocean[5][6]sea level | ||||
| Admission to Union | July 26, 1788 (11th) | ||||
| Governor | Andrew Cuomo (D) | ||||
| Lieutenant Governor | Robert Duffy (D) | ||||
| Legislature | New York Legislature | ||||
| – Upper house | State Senate | ||||
| – Lower house | State Assembly | ||||
| U.S. Senators | Charles Schumer (D)Kirsten Gillibrand (D) | ||||
| U.S. House delegation | 21 Democrats,8 Republicans(list) | ||||
| Time zone | Eastern: UTC-5/-4 | ||||
| Abbreviations | NY US-NY | ||||
| Website | ny.gov | ||||
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation’s third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east. The state has a maritime border with Rhode Island east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Ontario to the north and west, and Quebec to the north. The state of New York is often referred to as New York State to distinguish it from the city of New York.
New York City, with a population of over 8.1 million, is the most populous city in the United States. It is known for its status as a financial, cultural, transportation, and manufacturing center, and for its history as a gateway for immigration to the United States. According to the U.S. Department of Commerce, it is also a destination of choice for many foreign visitors. Both the state and city were named for the 17th century Duke of York, James Stuart, future James II and VII of England and Scotland.
New York was inhabited by various tribes of Algonquian and Iroquoian speaking Native American tribes at the time Dutch settlers moved into the region in the early 17th century. In 1609, the region was first claimed by Henry Hudson for the Dutch. Fort Nassau was built near the site of the present-day capital of Albany in 1614. The Dutch soon also settled New Amsterdam and parts of the Hudson River Valley, establishing the colony of New Netherland. The British took over the colony by annexation in 1664.
The borders of the British colony, the Province of New York, were roughly similar to those of the present-day state. About one third of all the battles of the Revolutionary War took place in New York. New York became an independent state on July 9, 1776, and enacted its constitution in 1777. The state ratified the United States Constitution on July 26, 1788, to become the 11th member of the United States.
HistoryMain article: History of New York 17th century
See also: Province of New YorkDuring the 17th century, Dutch trading posts established for the trade of pelts from the Lenape, Iroquois and other indigenous peoples expanded into the colony of New Netherland. The first of these trading posts were Fort Nassau (1614, near present-day Albany); Fort Orange (1624, on the Hudson River just south of the current city of Albany and created to replace Fort Nassau), developing into settlement Beverwijck (1647), and into what became Albany; Fort Amsterdam (1625, to develop into the town New Amsterdam which is present-day New York City); and Esopus, (1653, now Kingston). The success of the patroonship of Rensselaerswyck (1630), which surrounded Albany and lasted until the mid 19th century, was also a key factor in the early success of the colony. The British captured the colony during the Second Anglo-Dutch War and governed it as the Province of New York.
American Revolution
![]() New York in 1777
New York in 1777
The Sons of Liberty were organized in New York City during the 1760s, largely in response to the oppressive Stamp Act passed by the British Parliament in 1765. The Stamp Act Congress met in the city on October 19 of that year: a gathering of representatives from across the Thirteen Colonies that set the stage for the Continental Congress to follow. The Stamp Act Congress resulted in the Declaration of Rights and Grievances, which was the first written expression by representatives of the Americans of many of the rights and complaints later expressed in the United States Declaration of Independence, including the right to representative government.
The Capture of Fort Ticonderoga provided the cannon and gunpowder necessary to force a British withdrawal from the Siege of Boston in 1775.
New York endorsed the Declaration of Independence on July 9, 1776.[7] The New York state constitution was framed by a convention which assembled at White Plains, New York on July 10, 1776, and after repeated adjournments and changes of location, terminated its labors at Kingston, New York on Sunday evening, April 20, 1777, when the new constitution drafted by John Jay was adopted with but one dissenting vote. It was not submitted to the people for ratification. On July 30, 1777, George Clinton was inaugurated as the first Governor of New York at Kingston.
The first major battle of the American Revolutionary War after independence was declared—and the largest battle of the entire war—was fought in New York at the Battle of Long Island (a.k.a Battle of Brooklyn) in August of 1776. British victory made New York City their military and political base of operations in North America for the duration of the conflict, and consequently the center of attention for General George Washington’s intelligence network.
The notorious British prison ships of Wallabout Bay saw more American combatants die of intentional neglect than were killed in combat in every battle of the war, combined.
The first of two major British armies were captured by the Continental Army at the Battle of Saratoga in 1777, influencing France to ally with the revolutionaries.
In an attempt to retain their sovereignty and remain an independent nation positioned between the new United States and British North America, four of the Iroquois nations fought on the side of the British; only the Oneidas and their dependents the Tuscaroras allied themselves to the Americans.[8] The Sullivan Expedition of 1778 and 1779 destroyed nearly 50 Iroquois villages and adjacent croplands, forcing many refugees to British-held Niagara.[9] As allies of the British, the Iroquois were resettled in Canada after the war. In the treaty settlement, the British ceded most Indian lands to the new United States. Because New York made treaty with the Iroquois without getting Congressional approval, some of the land purchases are the subject of modern-day claims by the individual tribes. More than 5 million acres (20,000 km2) of former Iroquois territory was put up for sale in the years after the Revolutionary War, leading to rapid development in upstate New York.[10] As per the Treaty of Paris, the last vestige of British authority in the former Thirteen Colonies—their troops in New York City—departed in 1783, which was long afterwards celebrated as Evacuation Day.[11]
Following heated debate, which included the publication of the now quintessential constitutional interpretation—the Federalist Papers—as a series of installments in New York City newspapers, New York was the 11th state to ratify the United States Constitution, on July 26, 1788.[12]
19th century
![]() The creation of the Erie Canal led to rapid industrialization in New York.
The creation of the Erie Canal led to rapid industrialization in New York.
Transportation in western New York was difficult before canals were built in the early part of the 19th century. The Hudson and Mohawk Rivers could be navigated only as far as Central New York. While the St. Lawrence River could be navigated to Lake Ontario, the way westward to the other Great Lakes was blocked by Niagara Falls, and so the only route to western New York was over land.
Governor DeWitt Clinton strongly advocated building a canal to connect the Hudson River with Lake Erie, and thus all the Great Lakes. Work commenced in 1817, and the Erie Canal was finished in 1825. It was considered an engineering marvel. Packet boats traveled up and down the canal with sightseers and visitors on board.[13] The canal opened up vast areas of New York to commerce and settlement. It enabled Great Lakes port cities such as Buffalo and Rochester to grow and prosper. It also connected the burgeoning agricultural production of the Midwest and shipping on the Great Lakes, with the port of New York City. Improving transportation, it enabled additional population migration to territories west of New York.
Ellis IslandMain article: Ellis Island
![]()
![]() Scenes at the Immigration Depot and a nearby dock on Ellis Island
Scenes at the Immigration Depot and a nearby dock on Ellis Island
![]() Ellis Island in 1905
Ellis Island in 1905
Ellis Island was the main facility for immigrants, entering the United States in the late 19th century to the mid 20th century. It was opened when the federal government took over the responsibility for processing immigrants, prior to that it was the responsibility of the states. It replaced the prior New York State immigration center located at Castle Clinton, a War of 1812 era fort located in what is today Battery Park, through which at least 8 million immigrants such as Harry Houdini, passed through from 1855–1890.[14]
Ellis Island operated as an immigration center from January 1, 1892, until November 12, 1954. It is owned by the Federal government and is now part of the Statue of Liberty National Monument, under the jurisdiction of the National Park Service. It is situated in New York Harbor, between two states and cities, Jersey City, New Jersey and New York City, New York.
More than 12 million immigrants passed through Ellis Island, between 1892 and 1954. After 1924, when the National Origins Act was passed, the only immigrants to pass through there were displaced persons or war refugees.[15] Today, over 100 million Americans can trace their ancestry to the immigrants, who first arrived in America through Castle Clinton and Ellis Island, before dispersing to points all over the country. Ellis Island was the subject of a border dispute between New York State and New Jersey. The issue was settled in 1998 by the U.S. Supreme Court which ruled that the original 3.3 acre island was New York State territory and that the balance of the 27.5 acres (11 ha) added after 1834 by landfill was in New Jersey.
Statue of LibertyMain article: Statue of Liberty
![]() Statue of Liberty
Statue of Liberty
The Statue of Liberty was a gift from France to the United States to mark the Centennial of the American Declaration of Independence. The idea of giving a colossal representation of republican virtues to a "sister" republic, across the sea, served as a focus for the republican cause against other politicians. The Statue of Liberty was dedicated in New York Harbor on October 28, 1886.
Liberty Island closed on September 11, 2001; the island reopened in December, the monument reopened on August 3, 2004, but the statue remained closed until the summer of 2009. The National Park Service claims that the statue is not shut because of a terrorist threat, but principally because of a long list of fire regulation contraventions, including inadequate evacuation procedures. The museum and ten-story pedestal are open for visitors, but are only accessible if visitors have a "Monument Access Pass", which is a reservation that visitors must make in advance of their visit and pick up before boarding the ferry. There are a maximum of 3000 passes available each day, with a total of 15,000 visitors to the island daily. The interior of the statue remains closed, although a glass ceiling in the pedestal allows for views of Gustave Eiffel’s iron framework of Lady Liberty.
GeographyMain article: Geography of New York New York terrain.
New York terrain. Map of the Hudson and Mohawk rivers.
Map of the Hudson and Mohawk rivers.
New York covers 54,556 square miles (141,300 km2) and ranks as the 27th largest state by size.[2] The Great Appalachian Valley dominates eastern New York, while Lake Champlain is the chief northern feature of the valley, which also includes the Hudson River flowing southward to the Atlantic Ocean. The rugged Adirondack Mountains, with vast tracts of wilderness, lie west of the valley.
Most of the southern part of the state is on the Allegheny Plateau, which rises from the southeast to the Catskill Mountains. The western section of the state is drained by the Allegheny River and rivers of the Susquehanna and Delaware systems. The Delaware River Basin Compact, signed in 1961 by New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and the federal government, regulates the utilization of water of the Delaware system. The highest elevation in New York is Mount Marcy in the Adirondacks.[16]
New York’s borders touch (clockwise from the west) two Great Lakes (Erie and Ontario, which are connected by the Niagara River); the provinces of Ontario and Quebec in Canada; Lake Champlain; three New England states (Vermont, Massachusetts, and Connecticut); the Atlantic Ocean, and two Mid-Atlantic States, New Jersey and Pennsylvania. In addition, Rhode Island shares a water border with New York. New York is the only state that touches both the Great Lakes and the Atlantic Ocean, and is the second-largest of the original Thirteen Colonies.
In contrast with New York City’s urban atmosphere, the vast majority of the state is dominated by farms, forests, rivers, mountains, and lakes. New York’s Adirondack Park is the largest state park in the United States. It is larger than the Yellowstone, Yosemite, Grand Canyon, Glacier and Olympic National Parks combined.[17] New York established the first state park in the United States at Niagara Falls in 1885. Niagara Falls, on the Niagara River as it flows from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario, is a popular attraction.
The Hudson River begins at Lake Tear of the Clouds and flows south through the eastern part of the state without draining Lakes George or Champlain. Lake George empties at its north end into Lake Champlain, whose northern end extends into Canada, where it drains into the Richelieu and then the St. Lawrence Rivers. Four of New York City’s five boroughs are on three islands at the mouth of the Hudson River: Manhattan Island; Staten Island; and Long Island, which contains Brooklyn and Queens on its western end.
Upstate and downstate are often used informally to distinguish New York City or its greater metropolitan area from the rest of New York state. The placement of a boundary between the two is a matter of great contention.[18] Unofficial and loosely defined regions of Upstate New York include the Southern Tier, which often includes the counties along the border with Pennsylvania,[19] and the North Country, which can mean anything from the strip along the Canadian border to everything north of the Mohawk River.[20]
ClimateMain article: Climate of New York
![]() Lake-effect snow is a major contributor to snowfall totals in western New York.
Lake-effect snow is a major contributor to snowfall totals in western New York.
In general, New York has a humid continental climate, though under the Köppen climate classification, New York City has a humid subtropical climate.[21] Weather in New York is heavily influenced by two continental air masses: a warm, humid one from the southwest and a cold, dry one from the northwest.
The winters are long and cold in the Plateau Divisions of the state. In the majority of winter seasons, a temperature of −13 °F (−25 °C) or lower can be expected in the northern highlands (Northern Plateau) and 5 °F (−15 °C) or colder in the southwestern and east-central highlands (Southern Plateau). The summer climate is cool in the Adirondacks, Catskills and higher elevations of the Southern Plateau.
The New York City/Long Island area and lower portions of the Hudson Valley have rather warm summers by comparison, with some periods of high, uncomfortable humidity. The remainder of New York State enjoys pleasantly warm summers, marred by only occasional, brief intervals of sultry conditions. Summer daytime temperatures usually range from the upper 70s to mid 80s °F (25 to 30 °C), over much of the state.
New York ranks 46th among the 50 states in the amount of greenhouse gases generated per person. This relative efficiency is primarily due to the state’s higher rate of mass transit use.[22]
State parksSee also: List of New York state parks and New York State Office of Parks, Recreation and Historic Preservation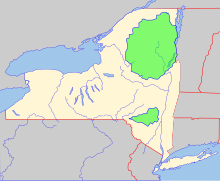
![]() Two major parks in the state are the Adirondack Park and Catskill Park.
Two major parks in the state are the Adirondack Park and Catskill Park.
New York has many state parks and two major forest preserves. Adirondack Park, roughly the size of the state of Vermont and the largest state park in the United States, was established in 1892 and given state constitutional protection to remain "forever wild" in 1894. The thinking that led to the creation of the Park first appeared in George Perkins Marsh’s Man and Nature, published in 1864. Marsh argued that deforestation could lead to desertification; referring to the clearing of once-lush lands surrounding the Mediterranean, he asserted "the operation of causes set in action by man has brought the face of the earth to a desolation almost as complete as that of the moon."
The Catskill Park was protected in legislation passed in 1885,[24] which declared that its land was to be conserved and never put up for sale or lease. Consisting of 700,000 acres (2,800 km2) of land,[24] the park is a habitat for bobcats, minks and fishers. There are some 400 black bears living in the region. The state operates numerous campgrounds and there are over 300 miles (480 km) of multi-use trails in the Park.
The Montauk Point State Park boasts the 1797 Montauk Lighthouse, commissioned under President George Washington, which is a major tourist attraction on the easternmost tip of Long Island. Hither Hills park offers camping and is a popular destination with surfcasting sport fishermen.
Counties
![]() Map of the counties in New YorkMain article: List of counties in New YorkSee also: Administrative divisions of New York
Map of the counties in New YorkMain article: List of counties in New YorkSee also: Administrative divisions of New York
New York is divided into 62 counties:
RegionsMain article: List of regions of the United States#New York
New York State is divided into eleven regions by the Department of Economic Development:[25]
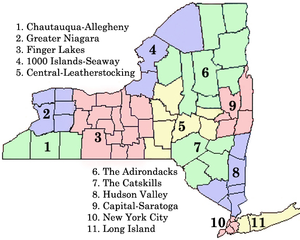
![]() Regions of New York as defined by the New York State Department of Economic Development
Regions of New York as defined by the New York State Department of Economic Development
New York State is sometimes divided into eight major regions:[26]
CitiesMain article: List of cities in New YorkFurther information: List of towns in New York, List of villages in New York, and List of census-designated places in New York
There are 62 cities in New York. The largest city in the state and the most populous city in the United States is New York City, which comprises five counties (boroughs): the Bronx, New York (Manhattan), Queens, Kings (Brooklyn), and Richmond (Staten Island). New York City is home to more than two-fifths of the state’s population.
The following are the ten largest cities in New York:[27]
The location of these cities within the state stays remarkably true to the major transportation and trade routes in the early 19th century, primarily the Erie Canal and railroads paralleling it. Today, Interstate 90 acts as a modern counterpart to commercial water routes.
Grouped by metropolitan statistical area,[28]the following are the twelve largest population centers in the state are:
The smallest city is Sherrill, New York, located just west of the Town of Vernon in Oneida County. Albany is the state capital, and the Town of Hempstead is the civil township with the largest population. If it were a city, it would be the second largest in the state with over 700,000 residents.
The southern tip of New York State—New York City, its suburbs including Long Island, the southern portion of the Hudson Valley, and most of northern New Jersey—can be considered to form the central core of the Northeast megalopolis", a super-city stretching from the northern suburbs of Boston south to the Virginia suburbs of Washington D.C..
Demographics
| Historical populations | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 340,120 | — | |
| 1800 | 589,051 | 73.2% | |
| 1810 | 959,049 | 62.8% | |
| 1820 | 1,372,812 | 43.1% | |
| 1830 | 1,918,608 | 39.8% | |
| 1840 | 2,428,921 | 26.6% | |
| 1850 | 3,097,394 | 27.5% | |
| 1860 | 3,880,735 | 25.3% | |
| 1870 | 4,382,759 | 12.9% | |
| 1880 | 5,082,871 | 16.0% | |
| 1890 | 5,003,174 | −1.6% | |
| 1900 | 7,268,894 | 45.3% | |
| 1910 | 9,113,614 | 25.4% | |
| 1920 | 10,385,227 | 14.0% | |
| 1930 | 12,588,066 | 21.2% | |
| 1940 | 13,479,142 | 7.1% | |
| 1950 | 14,830,192 | 10.0% | |
| 1960 | 16,782,304 | 13.2% | |
| 1970 | 18,236,967 | 8.7% | |
| 1980 | 17,558,072 | −3.7% | |
| 1990 | 17,990,455 | 2.5% | |
| 2000 | 18,976,457 | 5.5% | |
| 2010 | 19,378,102 | 2.1% | |
| Sources: 1910–2010[3] 1790–1900[29] | |||
Main article: Demographics of New York Population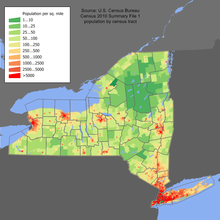
![]() New York population density map
New York population density map
As of 2006, New York was the third largest state in population after California and Texas,[30] with an estimated population of 19,541,453 as of July 1, 2009.[31] This represents an increase of 513,481, or 2.7%, since the last census in 2000.[32] It includes a natural increase since the last census of 803,680 people (that is 2,072,765 births minus 1,269,085 deaths) and a decrease due to net migration of 698,895 people out of the state.[32]Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 876,969 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 1,575,864 people.[32]
In spite of the open land in the state, New York’s population is very urban, with 92% of residents living in an urban area.[33]
New York is a slow growing state with a large rate of domestic migration to other states. In 2000 and 2005, more people moved from New York to Florida than from any one state to another.[34] However, New York state is one of the leading destinations for international immigration and thus has the second largest immigrant population in the country (after California) at 4.2 million as of 2008. Although Upstate New York receives considerable immigration, most of the state’s immigrants settle in and around New York City, due to its more vibrant economy and cosmopolitan culture.
The center of population of New York is located in Orange County, in the town of Deerpark.[35] New York City and its eight suburban counties (excluding those in New Jersey, Connecticut, and Pennsylvania) have a combined population of 13,209,006 people, or 68.42% of the state’s population.[36]
Racial and ancestral makeup![]() New York population ethnicity map
New York population ethnicity map
According to the US Census Bureau, the 2010 racial makeup of New York State was as follows:
- White – 65.7%
- Hispanic or Latino (of any race) – 17.6%
- Black or African American – 15.9%
- Asian – 7.3% (3.0% Chinese, 1.6% Indian, 0.7% Korean, 0.5% Filipino, 0.3% Pakistani, 0.3% Bangladeshi, 0.2% Japanese, 0.1% Vietnamese)
- Two or more races – 3.0%
- Native American/American Indian – 0.6%
The major ancestry groups in New York state are African American (15.8%), Italian (14.4%), Irish (12.9%), German (11.1%) and English (6%).[37] According to a 2004 estimate, 20.4% of the population is foreign-born.
New York is home to the largest African American population and the second largest Asian American population in the United States. In addition it is home to the largest Puerto Rican, Dominican and Jamaican American populations in the continental United States. The New York City neighborhood of Harlem has historically been a major cultural capital for African-Americans of sub-Saharan descent, and Bedford Stuyvesant is the largest such population in the United States.
Queens, also in New York City, is home to the state’s largest Asian-American population, and is also the most diverse county in the United States. The second concentration of Asian-Americans is in Manhattan’s Chinatown. Queens is home to the largest Andean population (Colombian, Ecuadorian, Peruvian and Bolivian) population in The United States of America.
In the 2000 Census, Italian Americans made up the largest ancestral group in Staten Island and Long Island, followed by Irish Americans. Albany and southeast-central New York also have populations with many of Irish-American and Italian-American descent. In Buffalo and western New York, German Americans are the largest group; in the northern tip of the state, French Canadians are. Americans of English ancestry are present throughout all of upstate New York. New York State has a higher number of Italian Americans than any other U.S. state.
6.5% of New York’s population were under 5 years of age, 24.7% under 18, and 12.9% were 65 or older. Females made up 51.8% of the population.
According to the 2000 U.S. Census, 13.61% of the population aged 5 and over speak Spanish at home, while 2.04% speak Chinese (including Cantonese and Mandarin), 1.65% Italian, and 1.23% Russian.[38]
Religion
Catholics comprise more than 40% of the population in New York.[39]Protestants are 30% of the population, Jews 8.4%, Muslims 3.5%, Buddhists 1%, and 13% claim no religious affiliation. The largest Protestant denominations are the United Methodist Church with 403,362; the American Baptist Churches USA with 203,297; and the Episcopal Church with 201,797 adherents.[40]
EconomyMain article: Economy of New York

![]() The New York Stock Exchange, the largest stock exchange in the world
The New York Stock Exchange, the largest stock exchange in the world

![]() Midtown Manhattan in New York City, the largest central business district in the United States
Midtown Manhattan in New York City, the largest central business district in the United States![]() A dairy farm in Brunswick
A dairy farm in Brunswick
New York’s gross state product in 2010 was $1.16 trillion, ranking third in size behind the larger states of California and Texas.[41] If New York were an independent nation, it would rank as the 16th largest economy in the world behind Turkey. Its 2007 per capita personal income was $46,364, placing it sixth in the nation behind Maryland, and eighth in the world behind Ireland. New York’s agricultural outputs are dairy products, cattle and other livestock, vegetables, nursery stock, and apples. Its industrial outputs are printing and publishing, scientific instruments, electric equipment, machinery, chemical products, and tourism.
A recent review by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities found 13 states, including several of the nation’s largest, face budget shortfalls for FY2009. New York faces a deficit that could be as large as $4.3 billion.[42]
New York exports a wide variety of goods such as foodstuffs, commodities, minerals, computers and electronics, cut diamonds, and automobile parts. In 2007, the state exported a total of $71.1 billion worth of goods, with the five largest foreign export markets being Canada ($15 billion), United Kingdom ($6 billion), Switzerland ($5.9 billion), Israel ($4.9 billion), and Hong Kong ($3.4 billion). New York’s largest imports are oil, gold, aluminum, natural gas, electricity, rough diamonds, and lumber.
Canada is a very important economic partner for the state. 21% of the state’s total worldwide exports went to Canada in 2007. Tourism from the north is also a large part of the economy. Canadians spent US$487 million in 2004 while visiting the state.
New York City is the leading center of banking, finance and communication in the United States and is the location of the New York Stock Exchange, the largest stock exchange in the world by dollar volume. Many of the world’s largest corporations are based in the city.
The state also has a large manufacturing sector that includes printing and the production of garments, furs, railroad equipment and bus line vehicles. Many of these industries are concentrated in upstate regions. Albany and the Hudson Valley are major centers of nanotechnology and microchip manufacturing, while the Rochester area is important in photographic equipment and imaging.
New York is a major agricultural producer, ranking among the top five states for agricultural products such as dairy, apples, cherries, cabbage, potatoes, onions, maple syrup and many others. The state is the largest producer of cabbage in the U.S. The state has about a quarter of its land in farms and produced US$3.4 billion in agricultural products in 2001. The south shore of Lake Ontario provides the right mix of soils and microclimate for many apple, cherry, plum, pear and peach orchards. Apples are also grown in the Hudson Valley and near Lake Champlain.
New York is the nation’s third-largest grape-producing state, behind California, and second-largest wine producer by volume. The south shore of Lake Erie and the southern Finger Lakes hillsides have many vineyards. In addition, the North Fork of Long Island developed vineyards, production and visitors’ facilities in the last three decades of the 20th century. In 2004, New York’s wine and grape industry brought US$6 billion into the state economy.
The state has 30,000 acres (120 km2) of vineyards, 212 wineries, and produced 200 million bottles of wine in 2004. A moderately sized saltwater commercial fishery is located along the Atlantic side of Long Island. The principal catches by value are clams, lobsters, squid, and flounder. These areas of the economy have been increasing as environmental protection has led to an increase in ocean wildlife.
As of January 2010, the state’s unemployment rate was 8.8%.[43]
TransportationMain article: Transportation in New York
 |

![]() The Thaddeus Kosciusko Bridge carries I-87 over the Mohawk River
The Thaddeus Kosciusko Bridge carries I-87 over the Mohawk River
![]() The New York City Subway serves more than 5 million rides on a given weekday
The New York City Subway serves more than 5 million rides on a given weekday
New York has one of the most extensive and one of the oldest transportation infrastructures in the country. Engineering difficulties because of the terrain of the state and the unique issues of the city brought on by urban crowding have had to be overcome since the state was young. Population expansion of the state generally followed the path of the early waterways, first the Hudson River and then the Erie Canal. Today, railroad lines and the New York State Thruway follow the same general route. The New York State Department of Transportation is often criticized for how they maintain the roads of the state in certain areas and for the fact that the tolls collected along the roadway have long passed their original purpose. Until 2006, tolls were collected on the Thruway within The City of Buffalo. They were dropped late in 2006 during the campaign for Governor (both candidates called for their removal).
In addition to New York City’s famous mass transit subway, four suburban commuter railroad systems enter and leave the city: the Long Island Rail Road, Metro-North Railroad, Port Authority Trans-Hudson, and five of New Jersey Transit’s rail lines. Many other cities have urban and regional public transportation. In Buffalo, the Niagara Frontier Transportation Authority runs the Buffalo Metro Rail light-rail system; in Rochester, the Rochester Subway operated from 1927 until 1956 but has fallen into disuse.
 License plate introduced on April 1, 2010 for vehicles registered in New York State.
License plate introduced on April 1, 2010 for vehicles registered in New York State. Former License plate design introduced in 2001
Former License plate design introduced in 2001
The New York State Department of Motor Vehicles (NYSDMV or DMV) is the governmental agency responsible for registering and inspecting automobiles and other motor vehicles as well as licensing drivers in the State of New York. As of 2008, the NYSDMV has 11,284,546 drivers licenses on file[44] and 10,697,644 vehicle registrations in force.[45] All gasoline powered vehicles registered in New York State must get an emissions inspection every 12 months. Diesel powered vehicles with a Gross Weight Rating over 8 500 lb that are registered in the NY Metropolitan Area must get an annual emissions inspection. All vehicles registered in NYS must get an annual safety inspection.
Portions of the transportation system are intermodal, allowing travelers to easily switch from one mode of transportation to another. One of the most notable examples is AirTrain JFK which allows rail passengers to travel directly to terminals at John F. Kennedy International Airport.
In May 2009 the New York City Department of Transportation under the control of Transportation Commissioner Janette Sadik-Khan banned cars from Times Square. The move designed to reduce pollution and pedestrian accidents looks likely to be implemented permantly, and will last at least until the end of the year.[46]
Politics and governmentMain article: Government of New York
![]() The New York State Capitol building in Albany.
The New York State Capitol building in Albany.
Under its present constitution (adopted in 1938), New York is governed by the same three branches that govern all fifty states of the United States: the executive branch, consisting of the Governor of New York and the other independently elected constitutional officers; the legislative branch, consisting of the bicameral New York State Legislature (senate and assembly); and the judicial branch, consisting of the state’s highest court, the New York Court of Appeals, and lower courts. The state has two U.S. senators, 29 members in the United States House of Representatives, and 31 electoral votes in national presidential elections (a drop from its 47 votes during the 1940s).
New York’s capital is Albany. The state’s subordinate political units are its 62 counties. Other officially incorporated governmental units are towns, cities, and villages. New York has more than 4,200 local governments that take one of these forms. About 52% of all revenue raised by local governments in the state is raised solely by the government of New York City, which is the largest municipal government in the United States, whereas New York City houses only 42% of the state population.[47]
The state has a strong imbalance of payments with the federal government. New York State receives 82 cents in services for every $1 it sends in taxes to the federal government in Washington.[48] The state ranks near the bottom, in 42nd place, in federal spending per tax dollar.[49]
Many of New York’s public services are carried out by public benefit corporations, frequently called authorities or development corporations. Well known public benefit corporations in New York include the Metropolitan Transportation Authority, which oversees New York City’s public transportation system, and the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey, a bi-state transportation infrastructure agency.
New York’s legal system is explicitly based upon English common Law.
Federal representationSee also: Current United States congressional delegation from New York and New York’s congressional districts
As of the 2000 census and the redistricting for the 2002 elections, the state has 29 members in the United States House of Representatives, and two U.S. senators. Two seats in the House will be lost in 2013 due to a decline in the state’s rate of population growth.[50] New York has 31 electoral votes in national presidential elections (a drop from its 47 votes during the 1940s).
New York is represented by Chuck Schumer and Kirsten Gillibrand in the United States Senate and has 29 representatives to the United States House of Representatives, behind California’s 53 congressional districts and Texas’ 32 congressional districts.
Capital punishmentMain article: Capital punishment in New York
Capital punishment was reintroduced in 1995 under the Pataki administration but the statute was declared unconstitutional in 2004, when the New York Court of Appeals ruled in People v. LaValle that it violated the state constitution. The remaining death sentence was commuted by the court to life imprisonment in 2007, in People v. John Taylor, and the death row was disestablished in 2008, under executive order from Governor Paterson. No execution has taken place in New York since 1963. Legislative efforts to amend the statute have failed, and death sentences are no longer sought at the state level, though certain crimes that fall under the jurisdiction of the federal government are subject to the federal death penalty.[51][52][53]
Politics
![]() Andrew Cuomo (D) is the current Governor of New York.Main articles: Politics of New York, Elections in New York, Political party strength in New York, and New York’s congressional districts
Andrew Cuomo (D) is the current Governor of New York.Main articles: Politics of New York, Elections in New York, Political party strength in New York, and New York’s congressional districts
In the last few decades, New York State has generally supported candidates belonging to the Democratic Party in national elections. Democratic presidential candidate Barack Obama won New York State by 25 percentage points in 2008, a bigger margin than John Kerry in 2004. New York City is a major Democratic stronghold with liberal politics. Many of the state’s other urban areas, such as Albany, Buffalo, Rochester, and Syracuse are also Democratic. Rural upstate New York, however, is generally more conservative than the cities and tends to favor Republicans. Heavily populated Suburban areas such as Westchester County and Long Island have swung between the major parties over the past 25 years, but more often than not support Democrats.
Same-sex marriages in New York were legalized on June 24, 2011 and were authorized to take place beginning 30 days thereafter.[54]
New York City is the most important source of political fund-raising in the United States for both major parties. Four of the top five zip codes in the nation for political contributions are in Manhattan. The top zip code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2000 presidential campaigns of both George W. Bush and Al Gore.[55]
EducationMain article: Education in New York
![]() System Administration Building of the State University of New York in Albany
System Administration Building of the State University of New York in Albany
The University of the State of New York oversees all public primary, middle-level, and secondary education in the state, while the New York City Department of Education manages the public school system in New York City. In 1894, reflecting general racial discrimination, the state passed a law that allowed communities to set up schools for children of African-American descent. In 1900, the state passed another law requiring integrated schools.[56]
At the college level, the statewide public university system is the State University of New York (SUNY). The City University of New York (CUNY) is the public university system of New York City. The SUNY system consists of 64 community colleges, technical colleges, undergraduate colleges and universities. The four university centers are University at Albany, Binghamton University, University at Buffalo and Stony Brook University.
In addition there are many notable private universities, including the oldest Catholic institution in the Northeast, Fordham University. New York is home to both Columbia University in New York City and Cornell University in Ithaca, making it the only state to contain more than one Ivy League school. West Point, the service academy of the U.S. Army is located just south of Newburgh, on the banks of the Hudson River.
During the 2007–2008 school year, New York spent more per pupil on public education than any other state.[57]
SportsMain article: Sports in New York
New York hosted the 1980 Winter Olympics at Lake Placid, the Games known for the USA–USSR hockey game dubbed the "Miracle on Ice" in which a group of American college students and amateurs defeated the heavily favored Soviet national ice hockey team 4–3 and went on to win the gold medal against Finland. Lake Placid also hosted the 1932 Winter Olympics. Along with St. Moritz, Switzerland and Innsbruck, Austria, it is one of the three places to have twice hosted the Winter Olympic Games.
New York is the home of one National Football League team, the Buffalo Bills (based in the suburb of Orchard Park). Although the New York Giants and New York Jets represent the New York metropolitan area and were previously located in New York City, they play in New Meadowlands Stadium, located in East Rutherford, New Jersey. The Meadowlands stadium will host Super Bowl XLVIII in 2014. There has been much controversy over several proposals for a new New York Jets football stadium. The owners of the New York Jets were willing to split the $1.5 billion cost of building a new football stadium over Manhattan’s West Side rail yards, but the proposal never came to fruition.
New York also has two Major League Baseball teams, the New York Yankees (based in the Bronx) and the New York Mets (based in Queens). New York is home to three National Hockey League franchises: the New York Rangers in Manhattan, the New York Islanders on Long Island and the Buffalo Sabres in Buffalo. New York has a National Basketball Association team, the New York Knicks, in Manhattan. The former New York Nets from 1968 to 1977 is now titled as a New Jersey team; however, plans to relocate to New York City are in the works. There are a variety of minor league teams that can be found all through the State of New York, such as the Long Island Ducks.
See also
|
- Outline of New York
- Bibliography of New York
- Index of New York-related articles
- List of National Register of Historic Places in New York
- List of New York state symbols
- List of people from New York
- List of places in New York
- USS New York
References
- ^ "New York State Motto". New York State Library. January 29, 2001. Archived from the original on June 8, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070608031632/http%3A//www.nysl.nysed.gov/emblems/motto.htm. Retrieved November 16, 2007.
- ^ a b "Land and Water Area of States (2000)". Infoplease.com. http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0108355.html. Retrieved April 11, 2008. Note: This area is based on U.S. Census Bureau figures. Other sources such as The World Almanac and the Rand McNally World Atlas use an area of 49,576 square miles (128,400 km2), which would rank the state 30th.
- ^ a b "2010 Census: Resident Population Data". 2010. http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ "Marcy". NGS data sheet. U.S. National Geodetic Survey. http://www.ngs.noaa.gov/cgi-bin/ds_mark.prl?PidBox=PG2096. Retrieved October 20, 2011.
- ^ a b "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2001. http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html. Retrieved October 24, 2011.
- ^ a b Elevation adjusted to North American Vertical Datum of 1988.
- ^ "Declaration of Independence". history.com. Archived from the original on April 9, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080409165028/http%3A//www.history.com/minisites/fourthofjuly/viewPage%3FpageId%3D690. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ Alan Taylor (2006). The Divided Ground: Indians, Settlers, and the Northern Borderland of the American Revolution. Knopf. ISBN 978-0679454717.
- ^ "Sullivan/Clinton Interactive Map Set". http://www.sullivanclinton.com/mapset/shell.swf. Retrieved August 30, 2010.
- ^ Chen, David W. Battle Over Iroquois Land Claims Escalates [1] The New York Times. May 16, 2000. . Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ "Happy Evacuation Day". New York City Department of Parks and Recreation. http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_newsroom/daily_plants/daily_plant_main.php?id=19733. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ "New York’s Ratification". The U.S. Constitution Online. http://www.usconstitution.net/rat_ny.html. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ "The Erie Canal: A Brief History". New York State Canals. http://www.nyscanals.gov/cculture/history/. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ National Park Service: Castle Clinton
- ^ The Brown Quarterly, Volume 4, No. 1 (Fall 2000)—Ellis Island/Immigration Issue
- ^ "Elevations and Distances in the United States". U.S Geological Survey. April 29, 2005. http://erg.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html#Highest. Retrieved November 6, 2006.
- ^ About the Adirondack Park, Adirondack Park Agency. Retrieved July 1, 2009.
- ^ Eisenstadt, Peter, ed (2005). The Encyclopedia of New York State. Syracuse University Press. p. 1619. ISBN 9780-8156-08080.
- ^ Eisenstadt, Peter, ed (2005). The Encyclopedia of New York State. Syracuse University Press. p. 1437. ISBN 9780-8156-08080.
- ^ Eisenstadt, Peter, ed (2005). The Encyclopedia of New York State. Syracuse University Press. p. 1119. ISBN 9780-8156-08080.
- ^ "Climate of New York". New York State Climate Office – Cornell University. http://nysc.eas.cornell.edu/climate_of_ny.html. Retrieved April 10, 2008.
- ^ The New York Post (June 3, 2007). "A Breath of Fresh New York Air". http://www.nypost.com/seven/06032007/news/regionalnews/a_breath_of_fresh_n_y__air_regionalnews_.htm. Retrieved June 6, 2007.
- ^ "Typical High and Low Temperatures For Various New York Cities". US Travel Weather. http://www.ustravelweather.com/new-york/. Retrieved March 24, 2010.
- ^ a b "Catskill Park History". catskillpark.org. Archived from the original on July 5, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080705134653/http://www.catskillpark.org/history/history.htm. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ "Map of eleven regions". Visitnewyorkstate.net. http://www.visitnewyorkstate.net/regions/. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ "Map of the eight regions of New York". Nyeducationjobs.com. http://www.nyeducationjobs.com/Information%20Resources/members_new_york_map.htm. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ "New York: History, Geography, Population, and State Facts". Infoplease.com. http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0108252.html. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Population of Metropolitan and Micropolitan Statistical Areas: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2007 (CBSA-EST2007-01)" (CSV). 2007 Population Estimates. United States Census Bureau, Population Division. March 27, 2007. Archived from the original on April 2, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080402204232/http%3A//www.census.gov/population/www/estimates/metro_general/2007/CBSA-EST2007-07.csv. Retrieved March 27, 2007.
- ^ "New York: 2000 (Population and Housing Unit Counts)" (PDF). 2000 United States Census. United States Census Bureau. 2000. http://www.census.gov/prod/cen2000/phc-3-34.pdf. Retrieved September 18, 2010. (page 1 of the document, page 31 of the file)
- ^ "Estimates of Population Change for the United States and States, and for Puerto Rico and State Rankings: July 1, 2005 to July 1, 2006" (Excel Spreadsheet). Archived from the original on March 11, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20070311040559/http%3A//www.census.gov/Press-Release/www/2006/statepopest_table1.xls. Retrieved January 5, 2007.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for the United States, Regions, States, and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2009". United States Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/popest/states/tables/NST-EST2009-01.csv. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- ^ a b c U.S. Census Bureau (December 15, 2008). "Cumulative Estimates of the Components of Population Change for the United States, Regions and States: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008 (NST-EST2008-04)" (CSV). http://www.census.gov/popest/states/tables/NST-EST2008-04.csv. Retrieved January 16, 2009.
- ^ Timothy S. Parker (September 10, 2010). "New York Fact Sheet: NY agriculture income population food education employment farms top commodities exports counties financial indicators poverty organic farming farm income America USDA". Ers.usda.gov. http://www.ers.usda.gov/StateFacts/NY.htm. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ "Domestic Migration Flows for States from the 2005 ACS" (Microsoft Word). Archived from the original on October 25, 2007. http://web.archive.org/web/20071025032612/http://www.census.gov/acs/www/Downloads/State_Migration_Flows_Paper.doc. Retrieved October 19, 2007.
- ^ "Population and Population Centers by State: 2000" (Text). http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/statecenters.txt. Retrieved January 5, 2007.
- ^ "DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000, Geographic Area: New York". U.S. Census Bureau, Census 2000. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?-geo_id=04000US36&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_DP3&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U. Retrieved January 5, 2007.
- ^ Awesome America: New York. Retrieved August 18, 2007.
- ^ "Language Map Data Center". Mla.org. July 17, 2007. http://www.mla.org/map_data_results&state_id=36&mode=state_tops. Retrieved July 2, 2010.
- ^ Egon Mayer, PhD; Barry A. Kosmin, PhD, Ariela Keysar, PhD (2001). "American Religious Identification Survey(Key Findings)". The City University of New York. http://www.gc.cuny.edu/faculty/research_briefs/aris/key_findings.htm. Retrieved January 5, 2007.
- ^ "The Association of Religion Data Archives | Maps & Reports". Thearda.com. http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/36_2000.asp. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ [greyhill.com/gdp-by-state "GDP by State"]. Greyhill Advisors. greyhill.com/gdp-by-state. Retrieved September 8, 2011.
- ^ 13 States Face Total Budget Shortfall of at Least $23 Billion in 2009; 11 Others Expect Budget Problems, December 18, 2007, Center on Budget and Policy Priorities
- ^ Bls.gov; Local Area Unemployment Statistics
- ^ "NYS DMV – Statistics – NYS Driver Licenses on File – 2008". Nydmv.state.ny.us. http://www.nydmv.state.ny.us/Statistics/statli08.htm. Retrieved July 2, 2010.
- ^ "NYS DMV – Statistics – Vehicle Registrations in Force – 2008". Nydmv.state.ny.us. http://www.nydmv.state.ny.us/Statistics/regin08.htm. Retrieved July 2, 2010.
- ^ "New York celebrates new era as cars are banished from Times Square". London: MailOnline. May 26, 2009. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/worldnews/article-1187300/New-York-celebrates-new-era-cars-banished-Times-Square.html. Retrieved May 25, 2009.
- ^ Office of the New York State Comptroller (2006-11). "2006 Annual Report on Local Governments" (PDF). http://www.osc.state.ny.us/localgov/datanstat/annreport/06annreport.pdf. Retrieved November 14, 2006.
- ^ New York City Finance Division (March 11, 2005). "A Fair Share State Budget: Does Albany Play Fair with NYC?". http://webdocs.nyccouncil.info/attachments/65379.htm?CFID=232457&CFTOKEN=33008944. Retrieved July 19, 2006.
- ^ "Federal Spending in Each State Per Dollar of Federal Taxes FY2005". Tax Foundation. http://www.taxfoundation.org/research/show/266.html. Retrieved April 12, 2008.
- ^ Rey, Jay (December 22, 2010). "N.Y.’s slow growth will mean loss of two seats in House". The Buffalo News. Retrieved December 22, 2010.
- ^ Rob Gallagher (October 25, 2005). "New York Executions". Archived from the original on May 28, 2008. http://web.archive.org/web/20080528081537/http%3A//users.bestweb.net/%7Erg/execution/NEW%2520YORK.htm. Retrieved April 9, 2009.
- ^ Scott, Brendan (July 24, 2008). "GOV PULLS SWITCH ON DEATH CELL". New York Post. http://www.nypost.com/seven/07242008/news/regionalnews/gov_pulls_switch_on_death_cell_121295.htm. Retrieved April 9, 2009.
- ^ Powell, Michael (April 13, 2005). "In N.Y., Lawmakers Vote Not to Reinstate Capital Punishment". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/articles/A47871-2005Apr12.html. Retrieved April 11, 2008.
- ^ Nicholas Confessore and Michael Barbaro (June 24, 2011). "New York Allows Same-Sex Marriage, Becoming Largest State to Pass Law". The New York Times Company. http://www.nytimes.com/2011/06/25/nyregion/gay-marriage-approved-by-new-york-senate.html?_r=1&hp. Retrieved June 25, 2011.
- ^ Opensecrets.org (May 16, 2005). "2006 Election Overview: Top Zip codes". http://www.opensecrets.org/bigpicture/topzips.asp?cycle=2004. Retrieved July 19, 2006.
- ^ Martha A. Sandweiss, Passing Strange: A Gilded Age Tale of Love and Deception Across the Color Line, New York: Penguin Press, 2009, pp. 213
- ^ Thomas, G. Scott (June 28, 2010). "New York Leads Nation in Education Spending". The Business Review (American City Business Journals, Inc). http://albany.bizjournals.com/albany/stories/2010/06/28/daily2.html. Retrieved June 29, 2010.
Further readingMain article: Bibliography of New York
- French, John Homer (1860). Historical and statistical gazetteer of New York State. Syracuse, New York: R. Pearsall Smith. OCLC 224691273. http://books.google.com/?id=R_zHwh4xByQC.
- New York State Historical Association (1940). New York: A Guide to the Empire State. New York City: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9781603540315. OCLC 504264143. http://books.google.com/?id=TmbOZd4D-ccC.
Note: Linked titles redirect to a free, full-view version hosted by Google Books or the Internet Archive. External links
| Find more about New York on Wikipedia’s sister projects: | |
| Definitions from Wiktionary | |
| Images and media from Commons | |
| Learning resources from Wikiversity | |
| News stories from Wikinews | |
| Quotations from Wikiquote | |
| Source texts from Wikisource | |
| Textbooks from Wikibooks | |
| OpenStreetMap has geographic data related to: New York |
General
- New York at the Open Directory Project
Government
- State Government website
- Governor
- New York State Senate
- New York State Assembly
- New York State Unified Court System
- Constitution of New York (or see
 Wikisource)
Wikisource)
Tourism and recreation
- New York (state) travel guide from Wikitravel
- I ♥ New York
- New York State Office of Parks, Recreation, and Historic Preservation
Culture and history
- New York State Historical Association
- New York State Cultural Education Center
- New York State Guide from the Library of Congress
- Over 350 Photos of Old New York City (1890–1990)
Maps and Demographics
- USGS geographic resources of New York
- New York State Climate Office (NOAA and Cornell University)
- New York State Fact Sheet
- 2000 Census of Population and Housing for New York, U.S. Census Bureau
- OPENCities Monitor participant
Coordinates: 43°N 75°W / 43°N 75°W / 43; -75 (New York)





