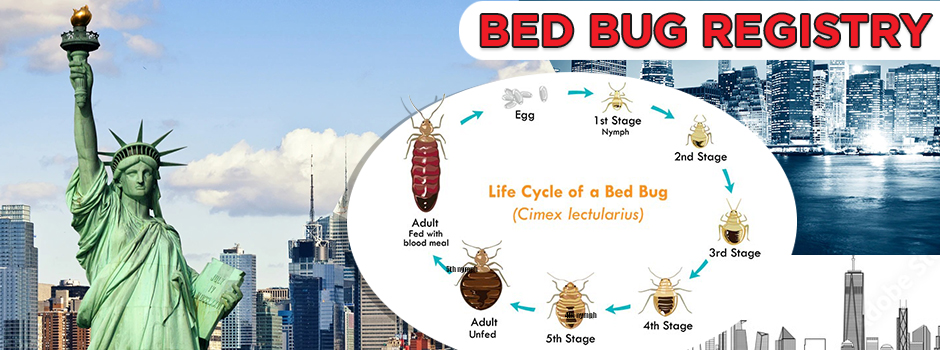
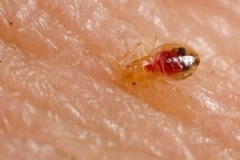
Bed Bug Feeding Blood
 The Bedbugs are live strictly by feeding on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. The name 'bed bug' is derived from the insect's preferred habitat infesting houses and especially beds or other common areas where people may sleep. Bedbugs, though not strictly nocturnal, are mainly active at night and are capable of feeding unnoticed on their hosts.
The Bedbugs are live strictly by feeding on the blood of humans and other warm-blooded animals. The name 'bed bug' is derived from the insect's preferred habitat infesting houses and especially beds or other common areas where people may sleep. Bedbugs, though not strictly nocturnal, are mainly active at night and are capable of feeding unnoticed on their hosts.
Bedbugs are bloodsucking insects. They are normally out at night just before dawn, with a peak feeding period of about an hour before sunrise. Bedbugs may attempt to feed at other times if given the opportunity and have been observed feeding during all periods of the day. They reach their host by walking, or sometimes climb the walls to the ceiling and drop down on feeling a heat wave. Bedbugs are attracted to their hosts by warmth and the presence of carbon dioxide. The bug pierces the skin of its host with two hollow feeding tubes. With one tube it injects its saliva, which contains anticoagulants and anesthetics, while with the other it withdraws the blood of its host. After feeding for about five minutes, the bug returns to its hiding place. The bites cannot usually be felt until some minutes or hours later, as a dermatological reaction to the injected agents, and the first indication of a bite usually comes from the desire to scratch the bite site. Because of their natural aversion for sunlight, bedbugs come out at night.
Although bedbugs can live for a year or eighteen months without feeding, and purportedly up to three years in the case of the species Oeciacus vicarius (the cliff swallow bug), they normally try to feed every five to ten days. Bedbugs that go dormant for lack of food often live longer than a year, while well-fed specimens typically live six to nine months. At the 57th Annual Meeting of the Entomological Society of America in 2009, it was reported that newer generations of pesticide-resistant bedbugs in Virginia could survive only two months without feeding .Vermin and pets may also complicate a barrier strategy. Bedbugs prefer human hosts, but will resort to other warm-blooded hosts if humans are not available, and some species can live up to eighteen months without feeding at all. Anaphylactoid reactions produced by the injection of serum and other nonspecific proteins are observed and there is the possibility that the saliva of the bedbugs may cause anaphylactic shock in a small percentage of people. It is also possible that sustained feeding by bedbugs may lead to anemia. It is also important to watch for and treat any secondary bacterial infection.[citation needed] Systemic poisoning may occur if the bites are numerous.
Bed bugs feed on humans, usually at night when they are asleep. They feed by piercing the skin with their elongated mouthparts, which consist of two styles that normally fold under their body when at rest but fully extend during blood-meal feeding. One stylet has a groove that carries saliva into the wound, while the other has a groove through which body fluids from the host are taken in.
 A single feeding may take up to 10 minutes, and feels like a pin prick, but because feeding usually occurs at night when people are asleep they are not aware they have been bitten until afterwards. However, saliva injected during the feeding can later produce large swellings on the skin that itch and may become irritated and infected when scratched. Swelling may not develop until a day or more after feeding, and some people do not show symptoms. Bed bugs currently are not considered to be disease carriers.
A single feeding may take up to 10 minutes, and feels like a pin prick, but because feeding usually occurs at night when people are asleep they are not aware they have been bitten until afterwards. However, saliva injected during the feeding can later produce large swellings on the skin that itch and may become irritated and infected when scratched. Swelling may not develop until a day or more after feeding, and some people do not show symptoms. Bed bugs currently are not considered to be disease carriers.
Bed bugs can go without feeding for 80 to 140 days. Older stages of nymphs can survive longer without feeding than younger ones, and adults have survived without food for as long as 550 days. A bed bug can take six times its weight in blood, and feeding can take 3 to 10 minutes. Adults live about 10 months, and there can be up to 3 to 4 generations of bed bugs per year.
 All people are not equally sensitive to bed bug bites, so while some victims break out in rashes from the bites, other people may not display symptoms. When a reaction does occur, the results of feeding can be mild (a simple red spot) to severe (rash or even hives). Bed bugs have been discovered to harbor 28 different human pathogens, but fortunately, the transmission of these diseases to people has not been demonstrated. Dark blood spots on sheets and bedding may indicate bed bug feeding. Bed bugs will sometimes excrete while they are feeding. This results in darker (reddish or brownish) spots or smears placed on bed sheets, pillowcases and mattresses, or in nearby areas. This material is composed mostly of digested blood and the stains care very characteristic.
All people are not equally sensitive to bed bug bites, so while some victims break out in rashes from the bites, other people may not display symptoms. When a reaction does occur, the results of feeding can be mild (a simple red spot) to severe (rash or even hives). Bed bugs have been discovered to harbor 28 different human pathogens, but fortunately, the transmission of these diseases to people has not been demonstrated. Dark blood spots on sheets and bedding may indicate bed bug feeding. Bed bugs will sometimes excrete while they are feeding. This results in darker (reddish or brownish) spots or smears placed on bed sheets, pillowcases and mattresses, or in nearby areas. This material is composed mostly of digested blood and the stains care very characteristic.
- Treating Bed Bug With chemicals [Last Updated On: September 19th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 19th, 2022]
- Symptoms Picture Gallery [Last Updated On: September 20th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 20th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: September 21st, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 21st, 2022]
- Simplified Bed Bug Preparation [Last Updated On: September 22nd, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 22nd, 2022]
- Quality Pest Control Methods [Last Updated On: September 23rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 23rd, 2022]
- Pajamas Diminish Bed Bug Bites [Last Updated On: September 24th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 24th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Picture Gallery [Last Updated On: September 25th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 25th, 2022]
- Pesticides [Last Updated On: September 26th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 26th, 2022]
- Male and Female Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: September 27th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 27th, 2022]
- Affordable Bed Bug Registry Detection Method [Last Updated On: September 28th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 28th, 2022]
- Introduction About Bed Bug [Last Updated On: September 29th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 29th, 2022]
- Insect Bed Bug [Last Updated On: September 30th, 2022] [Originally Added On: September 30th, 2022]
- Welcome to Bed Bug Registry Database [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 1st, 2022]
- How to Kill Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 2nd, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 2nd, 2022]
- How Bed Bug Bite [Last Updated On: October 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 3rd, 2022]
- Get Rid of Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 4th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 4th, 2022]
- DDT for Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 5th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 5th, 2022]
- Control Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: October 6th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 6th, 2022]
- Contact Us [Last Updated On: October 7th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 7th, 2022]
- Box Spring Treatment [Last Updated On: October 8th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 8th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 9th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 9th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 10th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 10th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Wall or Baseboard [Last Updated On: October 11th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 11th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Videos [Last Updated On: December 5th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 12th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Treatment Synergy [Last Updated On: October 13th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 13th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Treatment and Removal, How it is done [Last Updated On: October 14th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 14th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Transmit Disease [Last Updated On: October 15th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 15th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Tape [Last Updated On: October 16th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 16th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 17th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 17th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Sniffing Dogs [Last Updated On: October 18th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 18th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Spray - Non Toxic [Last Updated On: October 19th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 19th, 2022]
- Bedbug Species [Last Updated On: October 20th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 21st, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 21st, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 22nd, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 22nd, 2022]
- Bed Bug Repellent [Last Updated On: October 24th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 24th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 25th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 25th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 26th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 26th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 27th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 27th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Pillow Case Encasement Covers [Last Updated On: October 29th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 29th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: October 30th, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 30th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Network [Last Updated On: October 31st, 2022] [Originally Added On: October 31st, 2022]
- Bed Bug Molting [Last Updated On: November 1st, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 1st, 2022]
- Bed Bug Mattress Encasement Protector Covers [Last Updated On: November 2nd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 2nd, 2022]
- Bed Bug Look Like [Last Updated On: November 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 3rd, 2022]
- Advanced Bed Bug Preparation [Last Updated On: November 4th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 4th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Wall or Baseboard [Last Updated On: November 5th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 5th, 2022]
- Bedbug Legislation [Last Updated On: November 6th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 6th, 2022]
- Bed bug Knowledge [Last Updated On: November 7th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 7th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 8th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 8th, 2022]
- Bedbug in Hotel [Last Updated On: November 9th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 9th, 2022]
- Bedbuig in Clothes, Fabrics [Last Updated On: November 11th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 11th, 2022]
- Bedbug History [Last Updated On: November 12th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 12th, 2022]
- Bedbug Hiding PLaces [Last Updated On: November 13th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 13th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Nesting Location [Last Updated On: November 14th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 14th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 15th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 15th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 17th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 17th, 2022]
- Bedbug Epidemic [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 18th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Eggs and Nymphs [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Distribute [Last Updated On: November 20th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 20th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Discrimination [Last Updated On: November 21st, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 21st, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 22nd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 22nd, 2022]
- Bed Bug Colony [Last Updated On: November 23rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 23rd, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 24th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 24th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 25th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 25th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Box Spring Encasement Covers [Last Updated On: November 26th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 26th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Bites Pictures [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2022]
- Bedbug Bites [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 28th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: November 29th, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 29th, 2022]
- Bed Bug Products [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: November 30th, 2022]
- Allergy Sentry Box Spring Encasement [Last Updated On: December 1st, 2022] [Originally Added On: December 1st, 2022]
- Affordable Bed Bug Detection Method [Last Updated On: December 5th, 2022] [Originally Added On: December 2nd, 2022]
- Advanced Bed Bug Preparation [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: December 3rd, 2022]
- Adult Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: December 3rd, 2022] [Originally Added On: December 4th, 2022]