Click Free Pest Control Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free pest control quote today.
Bed bugs and scabies can both spell trouble for you and your family. While bed bugs bite and can produce an uncomfortable rash, scabies is a skin condition caused by small mites that burrow under the skin. Both bed bug bites and scabies cause itching and discomfort that, while not life-threatening, can be unpleasant.
If you suspect you've either been bitten by a bed bug or may have scabies as a result of mites, it's important that you quickly figure out which has invaded your home so the issue can be resolved by a professional pest control specialist. The type of treatment a specialist recommends will depend on which bug has infested your home. (It's also important to visit a medical professional to receive a proper diagnosis and treatment for any symptoms as a result of a bite.)
Here's what you should know to help you identify the difference between bed bug and scabies.
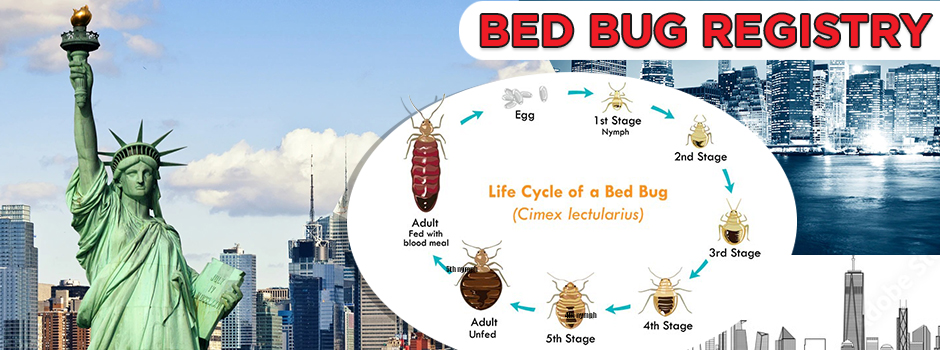
Bed bugs are small insects that feed on mammal blood. That means they can bite dogs, cats, humans and any other mammals living in your home. They typically enter your house by piggybacking on your luggage or traveling in used furniture, clothing and various soft items.
Although they can nest anywhere in your house, bed bugs typically take up residence along the seams of mattresses, inside walls and in furniture. As long as the space is dry and dark, they're happy to build a home there.
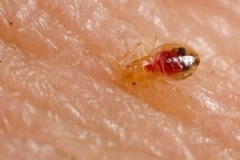
These bugs are small about the size of an apple seed and range in color from light brown to reddish-brown.
Bed bugs are insects, but scabies are actually arachnids. And while they feed on human blood, they don't do it by crawling around and biting the surface of your skin. Instead, they burrow into the outer layer of skin where they then lay and hatch their eggs.
Unlike bed bugs, scabies mites are invisible to the naked eye. They're microscopic parasites that you won't see even if they're crawling around on the surface of your skin. And since they're not insects in the traditional sense, you're going to need more than just pest control specialists to help treat them. Rather, you'll need to consult with your doctor or dermatologist to find the right treatment method.
Since scabies and bed bugs are different pests entirely, it makes sense that infestations of each are triggered by different factors. By understanding the difference between scabies and bed bug infestations, you'll be better prepared to handle or prevent infestations.
Contrary to what many believe, bed bug infestations aren't caused by a lack of hygiene or a lack of cleanliness around the home. Bed bugs are actually opportunistic and nomadic insects. They hitch rides on luggage when you stay in hotel rooms, come in on used furniture that you buy from local shops, online swap shops and classified ads, or travel in from close contact with infested areas in common areas like those found in dorms, buses, taxis and even cruise ships.
Anywhere that bed bugs are currently nesting is a place where you could pick them up, regardless of how clean you may keep your home.
Scabies infestations are a bit harder to predict and prevent than bed bug infestations. Scabies are most commonly spread by skin-to-skin contact with an infected person who has been bitten by a burrowing mite. But sometimes, scabies can be contracted by sharing clothing or bedding with an infected person. That's why it most commonly happens among people spending time in the same household, childcare or school groups.
While scabies are typically only spread via prolonged skin-to-skin contact, a more severe form called crusted scabies or Norwegian scabies is highly contagious.
Both bed bugs and scabies feed on your blood, but they do it in different ways. One feeds from the outside of your body and the other feeds from inside your body. Bed bugs use their specially developed mouth to suck your blood and then scurry off to their hiding spots, making them hard to detect unless you know what to look for. Scabies, on the other hand, burrow underneath your skin to feed and lay eggs.
Although their bites are both itchy, these pests have some additional, fairly notable differences you may need to watch out for.
Bed bugs are fairly easy to spot and identify if you know what they look like and what to expect from their bites. The most noticeable differences come from the types of bites and marks they leave behind.
These are a few of the common characteristics to watch for:
If you notice any of these signs, you may have a bed bug infestation in your home. Keep in mind that the infestation may be consolidated to a single room. Only a pest control specialist will be able to determine how severe the infestation is and identify the proper treatment protocol to address the infestation.
Because scabies are microscopic mites, spotting them with your naked eye isn't something you'll be able to do. Instead, you'll need to look for the common signs of a scabies infection on your skin. These include:
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's best to contact your doctor or dermatologist as soon as you can. The sooner you do, the sooner they can start treating the infection and relieve your symptoms.
At first glance, bed bug bites and scabies bite rashes can appear similar. But they're incredibly different when you start looking at the bites more closely. While the following images and information are designed to help you more easily identify a bed bug bite or a scabies bite, it's important to visit a medical professional to more accurately diagnose and treat a bite or rash in case it may be something more severe.
Bed bug bites are raised, flat red welts, sometimes appearing three in a row. For some people, the bites can resemble mosquito bites, but others who are more sensitive to the bites may experience swelling at the site as well.
Without bed bug treatment, new bites will continue to appear (but generally not worsen in appearance unless infection is present) as the infestation in your home grows. Bed bugs bite skin that is exposed during sleep, especially where the sheet or mattress meets the body. Bites typically occur around the shoulders, arms, legs, back and face.
Scabies don't bite you to eat you. Instead, they do it to burrow into your skin to lay eggs. These burrows appear as raised lines, either grey-ish white or skin colored. They eventually turn into red, inflamed bumps called papules and can fester if left untreated.
Scabies prefer to dig into warm, moist folds of skin and typically burrow between the fingers and toes, in armpits, under nail beds and around the waist and other sensitive areas. First-time scabies victims develop a rash and itching two to six weeks after exposure. If you've had scabies before, it typically only takes between one and four days for these same symptoms to occur.
Scabies typically cause a more intense itching, especially at night. This often leads to open sores and infections, though this can happen with bites from either bed bugs or scabies.
While scabies don't bite, but rather burrow, both bed bug bites and scabies cause the skin to become incredibly itchy. However, their symptoms are less similar than you might think.
Bed bug bites tend to occur in clusters, particularly around the knees, elbows and neck. But bed bugs can and will bite you anywhere if they get the opportunity.
You won't actually feel the bite itself. Instead, you'll feel discomfort after the bugs have already fed. For most people, this results in feelings of intense itchiness, similar to bad mosquito bites. In others, it can result in a slight burning sensation. If the bites become infected, often due to intense and repeated scratching, the site can become swollen, sore or bloody.
As noted before, scabies don't bite to eat our blood. Instead, scabies burrow into the skin to lay eggs. However, what you may assume to be scabies bites" tend to appear more rash-like and can happen anywhere on your body. Most people initially notice small, raised bumps, but as the infection progresses, the rash can develop a scaly, red, and swollen appearance.
The infection site is often very itchy, with symptoms becoming more severe at night.
If you suspect either bed bugs or scabies, it's normal to feel overwhelmed and concerned about the safety of your home and your family's well-being. And the more you research both bed bugs and scabies, the more questions you'll likely have.
Here are the answers to a few of the most common questions people ask so you can better prepare and educate yourself before seeking help for your infestation.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, scabies infestations are passed through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected individual or through prolonged exposure to clothing or bedding an infected person has used. So, while scabies mites could, in theory, live in a mattress, it's highly unlikely that you'd develop an infection just from the mattress alone. Instead, scabies mites prefer to live on skin where they have access to the nutrients they need to survive and can burrow into your skin to lay their eggs. These mites will not survive more than two or three days away from human skin.
If you're worried about catching scabies in bed, the best thing you can do is thoroughly wash and dry your bed linens. This should kill the mites.
Thankfully, bed bugs are not able to burrow under human skin to lay their eggs. Instead, they lay eggs in dark, dry areas like the seams along your mattress and inside pieces of furniture. Remember, bed bugs bite you on your skin. They don't burrow into it like scabies mites do.
Unfortunately, it is possible to have both bed bugs and scabies at the same time. As previously discussed, both insects feed on your blood, but they do so in different ways. Bed bugs bite you on the outside of your body and scabies burrow beneath your skin to feed. This means they're not in direct competition with each other and can (unfortunately) thrive at the same time.
Bed bugs do not cause scabies. In fact, bed bugs are not known to be vectors of disease pathogens or encourage other infestations in your home.
While bed bugs are not contagious, these pests can easily migrate from person to person, and from place to place. Bed bugs can hitch rides on clothing, luggage, and furniture and then infest your home and move from one home or room to another. Scabies, on the other hand, require prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person in order to be contagious. However, as mentioned previously, crusted or Norwegian scabies are highly contagious.
Bed bug infestations can last for years if left untreated since they breed and grow rapidly. However, adult bed bugs can live on their own for about 10 months. During that time, they can breed and the infestation can spread throughout your house.
Scabies mites can live for as long as two months on a human. And while it's possible for an infection to last longer than that, most people find the symptoms too uncomfortable to tolerate for more than a few weeks without seeking medical help.
Both bed bug infestations and scabies infections require professional help. But the treatment methods differ.
To get rid of a bed bug infestation, you'll need to consult with an experienced pest control specialist. Remember, bed bugs are true insects and, since they infest your house rather than your body, only an experienced pest control professional can help you eliminate them.
The type of treatment they'll use largely depends on the extent of the infestation and your home's unique needs. If you suspect a bed bug infestation, contact your pest control professional as soon as possible to schedule a consultation. They'll be able to check your home for bed bugs and develop a treatment plan so you and your family can get back to enjoying your home.
Although some people may think scabies mites are insects, they are not and not a creature that a pest control specialist can treat. You'll need to schedule an appointment with your doctor or dermatologist to treat the bites and the pest quickly. Depending on the severity of your infection, you may need prescription medications and antibiotics to help you get rid of the mites once and for all.
Once you do, it's a good idea to thoroughly clean any potentially infected items:
Although Terminix can't help you get rid of scabies (you'll need a doctor for that), our experienced pest control specialists can help you deal with a bed bug infestation in your home. Contact us as soon as you discover the first warning signs of a bed bug problem on your property and schedule a consultation. Our team will inspect your home, identify the bed bug hotspots and create a plan to help deal with the infestation.
Read more from the original source:
Bed Bugs vs Scabies: The Difference Between Them | Terminix
- Bed Bug Registry Database Wyoming, Usa, National Bed Bug ... [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Bed bugs!!! - Review of The Wort Hotel, Jackson, WY - TripAdvisor [Last Updated On: November 27th, 2013] [Originally Added On: November 27th, 2013]
- Do bed bugs live inside wooden beds? - Orkin [Last Updated On: December 24th, 2013] [Originally Added On: December 24th, 2013]
- 2014 Top Bed Bug Cities in the USA [Last Updated On: January 16th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 16th, 2014]
- Bed bugs!!! - Review of The Wort Hotel, Jackson, WY ... [Last Updated On: January 25th, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 25th, 2014]
- Wyoming Bed Bugs Control | Free Estimates | Bed Bugs Pest ... [Last Updated On: January 31st, 2014] [Originally Added On: January 31st, 2014]
- Bed bugs!!! - Review of Jackson, WY - TripAdvisor [Last Updated On: February 3rd, 2014] [Originally Added On: February 3rd, 2014]
- How Much Does It Cost To Get Rid Of Bed Bugs? Free Bed Bug ... [Last Updated On: June 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: June 2nd, 2014]
- Tenants Rights Bed Bugs | RPA Tenant Rights Blog [Last Updated On: June 2nd, 2014] [Originally Added On: June 2nd, 2014]
- Bed Bug Wyoming | Bed Bug Relief [Last Updated On: October 7th, 2014] [Originally Added On: October 7th, 2014]
- Bed bugs, lice found in schools - News - The Cumberland ... [Last Updated On: November 19th, 2014] [Originally Added On: November 19th, 2014]
- Bed bugs are biting: Can Casper stop them? [Last Updated On: December 16th, 2014] [Originally Added On: December 16th, 2014]
- Bedbug Infestation - What Causes Bed Bugs [Last Updated On: February 9th, 2015] [Originally Added On: February 9th, 2015]
- Local Resources for Bed Bug Assistance | Bed Bugs: Get ... [Last Updated On: August 7th, 2017] [Originally Added On: August 7th, 2017]
- Parsippany NJ Bed bug Hotel and Apartment Reports [Last Updated On: October 20th, 2017] [Originally Added On: October 20th, 2017]
- Durham NC Bed bug Hotel and Apartment Reports [Last Updated On: February 4th, 2018] [Originally Added On: February 4th, 2018]
- Mason OH Bed bug Hotel and Apartment Reports [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2018] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2018]
- Kill Bed Bugs in Wyoming WV Best of 2018 - chinanews-jp.com [Last Updated On: February 11th, 2018] [Originally Added On: February 11th, 2018]
- Cocoa Beach FL Bed bug Hotel and Apartment Reports [Last Updated On: February 24th, 2018] [Originally Added On: February 24th, 2018]
- Kill Bed Bugs Worland Wyoming Best of 2018 [Last Updated On: May 31st, 2018] [Originally Added On: May 31st, 2018]
- Pest Control in Wyoming | Rid Your Home Of Bed Bugs in ... [Last Updated On: May 31st, 2018] [Originally Added On: May 31st, 2018]
- Wyoming Bed Bug Hotel and Apartment Reports ... [Last Updated On: January 17th, 2020] [Originally Added On: January 17th, 2020]
- Concern over reported bedbug situation at West Side CTC - wnep.com [Last Updated On: February 7th, 2020] [Originally Added On: February 7th, 2020]
- The 10 Best Bed Bug Exterminators in Wyoming, MI 2020 [Last Updated On: July 23rd, 2020] [Originally Added On: July 23rd, 2020]
- How To Check for Bed Bugs - Bed Bugs Wyoming - Bed Bugs ... [Last Updated On: July 31st, 2020] [Originally Added On: July 31st, 2020]
Click Free Exterminator Quote
to fill in a form to obtain a free exterminator quote today.