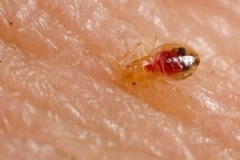
We cannot vouch for the truthfulness of any report on this site. If you feel a location has been reported in error, or want to dispute a report, please contact us.
Yukon Territory /jukn/ or the Yukon is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The word Yukon means "Great River" in Gwichin. The territory's capital is Whitehorse.
The territory was created in 1898 as the Yukon. The federal government's most recent update of the Yukon Act in 2003 confirmed "Yukon", rather than "Yukon Territory", as the current usage standard. The largest ethnic group in the territory is English, followed by First Nations. Yukon law recognizes First Nations languages, but only considers French and English as official languages.
At 5,959 metres (19,551ft), Yukon's Mount Logan, in Kluane National Park and Reserve, is the highest mountain in Canada and the second-highest of North America (after Mount McKinley in the U.S. state of Alaska). The territory's climate is Arctic and subarctic, resulting in long cold winters, short summers, and little precipitation.
The sparsely populated Yukon abounds with snow-melt lakes and perennially snow-capped mountains. Although the climate is Arctic and subarctic and very dry, with long, cold winters, the long sunshine hours in short summer allow hardy crops and vegetables, flowers and fruit to grow.
The territory is the approximate shape of a right triangle, bordering the U.S. state of Alaska to the west for 1,210km (752 miles) mostly along longitude 141 W, the Northwest Territories to the east and British Columbia to the south. Its northern coast is on the Beaufort Sea. Its ragged eastern boundary mostly follows the divide between the Yukon Basin and the Mackenzie River drainage basin to the east in the Mackenzie mountains. Whitehorse is the territorial capital.
Most of the territory is in the watershed of its namesake, the Yukon River. The southern Yukon is dotted with a large number of large, long and narrow glacier-fed alpine lakes, most of which flow into the Yukon River system. The larger lakes include Teslin Lake, Atlin Lake, Tagish Lake, Marsh Lake, Lake Laberge, Kusawa Lake and Kluane Lake. Bennett Lake on the Klondike Gold Rush trail is a lake flowing into Nares Lake, with the greater part of its area within the Yukon.
Canada's highest point, Mount Logan (5,959m/19,551 ft), is in the territory's southwest. Mount Logan and a large part of the Yukon's southwest are in Kluane National Park and Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Other national parks include Ivvavik National Park and Vuntut National Park in the north.
Other watersheds include the Mackenzie River and the AlsekTatshenshini, as well as a number of rivers flowing directly into the Beaufort Sea. The two main Yukon rivers flowing into the Mackenzie in the Northwest Territories are the Liard River in the southeast and the Peel River and its tributaries in the northeast.
Notable widespread tree species within the Yukon are the Black Spruce and White Spruce. Many trees are stunted because of the short growing season and severe climate.
Read more here:
Bed Bug Registry Database Yukon, Canada, National Bed Bug ...

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location