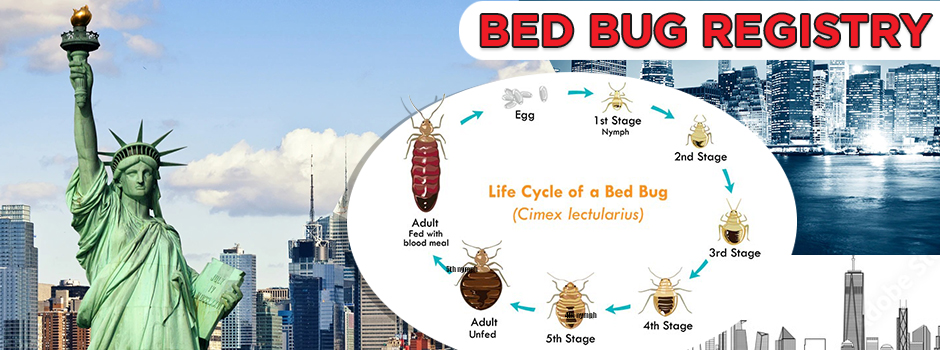
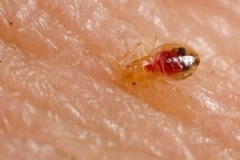
We cannot vouch for the truthfulness of any report on this site. If you feel a location has been reported in error, or want to dispute a report, please contact us.
Alabama (i /lbm/) is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States of America. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland waterways. The state ranks 23rd in population with almost 4.6million residents in 2006.
From the American Civil War until World War II, Alabama, like many Southern states, suffered economic hardship, in part because of continued dependence on agriculture. Despite the growth of major industries and urban centers, white rural interests dominated the state legislature until the 1960s, while urban interests and African Americans were under-represented. Following World War II, Alabama experienced growth as the economy of the state transitioned from agriculture to diversified interests in heavy manufacturing, mineral extraction, education, and technology. In addition, the establishment or expansion of multiple military installations, primarily those of the U.S. Army and U.S. Air Force, added to state jobs.
Alabama is unofficially nicknamed the Yellowhammer State, after the state bird. Alabama is also known as the "Heart of Dixie". The state tree is the Longleaf Pine, the state flower is the Camellia. The capital of Alabama is Montgomery. The largest city by population is Birmingham. The largest city by total land area is Huntsville. The oldest city is Mobile, founded by French colonists.
The Alabama, a Muskogean-speaking tribe whose members lived just below the confluence of the Coosa and Tallapoosa Rivers on the upper reaches of the Alabama River, served as the etymological source of the names of the river and state. In the Alabama language, the word for an Alabama person is Albaamo (or variously Albaama or Albamo in different dialects; the plural form "Alabama persons" is Albaamaha). The word Alabama is believed to have originated from the Choctaw language and was later adopted by the Alabama tribe as their name. The spelling of the word varies significantly between sources. The first usage appears in three accounts of the Hernando de Soto expedition of 1540 with Garcilasso de la Vega using Alibamo, while the Knight of Elvas and Rodrigo Ranjel wrote Alibamu and Limamu, respectively. As early as 1702, the tribe was known to the French as Alibamon with French maps identifying the river as Rivire des Alibamons. Other spellings of the appellation have included Alibamu, Alabamo, Albama, Alebamon, Alibama, Alibamou, Alabamu, and Allibamou.
Although the origin of Alabama could be discerned, sources disagree on its meaning. An 1842 article in the Jacksonville Republican originated the idea that the meaning was "Here We Rest." This notion was popularized in the 1850s through the writings of Alexander Beaufort Meek. Experts in the Muskogean languages have been unable to find any evidence to support such a translation. Scholars believe the word comes from the Choctaw alba (meaning "plants" or "weeds") and amo (meaning "to cut", "to trim", or "to gather"). The meaning may have been "clearers of the thicket" or "herb gatherers" which may refer to clearing of land for cultivation or to collecting medicinal plants.
Indigenous peoples of varying cultures lived in the area for thousands of years before European colonization. Trade with the Northeast via the Ohio River began during the Burial Mound Period (1000BCAD700) and continued until European contact. The agrarian Mississippian culture covered most of the state from 1000 to 1600 AD, with one of its major centers being at the Moundville Archaeological Site in Moundville, Alabama. Analysis of artifacts recovered from archaeological excavations at Moundville were the basis of scholars' formulating the characteristics of the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex (SECC). Contrary to popular belief, the SECC appears to have no direct links to Mesoamerican culture, but developed independently. The Ceremonial Complex represents a major component of the religion of the Mississippian peoples; it is one of the primary means by which their religion is understood.
Among the historical tribes of Native American people living in the area of present-day Alabama at the time of European contact were Iroquoian-speaking Cherokee, and Muskogean Alabama (Alibamu),Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek, Koasati, and Mobile.
The French founded the first European settlement in the present-day state at Mobile in 1702. Southern Alabama was French from 1702 to 1763, part of British West Florida from 1763 to 1780, and part of Spanish West Florida from 1780 to 1814.
Northern and central Alabama was part of British Georgia from 1763 to 1783 and part of the United States Mississippi Territory thereafter. Statehood was delayed by the territory's lack of a coastline; when Andrew Jackson captured Spanish Mobile in 1814, he claimed that area for the US and gained passage to the gulf. Alabama was the twenty-second state, admitted to the Union in 1819. Its constitution provided for universal suffrage for white men.
See original here:
Bed Bug Registry Database Alabama, Usa, National Bed Bug ...

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location