Detection Appearance
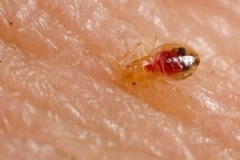
Adult bed bugs are light brown or reddish-brown, flattened, oval-shaped and have no hind wings. Their front wings are vestigial and reduced to pad-like structures. They have segmented abdomens with microscopic hairs that give them a banded appearance. Adults grow to 45 mm in length and 1.53 mm wide. Newly hatched nymphs are translucent, lighter in colour and become browner as they moult and reach maturity. Bed bugs may be mistaken for other insects, such as booklice, small cockroaches, or carpet beetles, however when warm and active, their movements are more ant-like. They emit a characteristic disagreeable odor when crushed.
Fleas are wingless insects 1.5 to 3.3 mm long. They are agile, usually dark colored (for example, the reddish-brown of the cat flea), with tube-like mouth-parts adapted to feeding on the blood of their hosts. Their legs are long, the hind pair well adapted for jumping: a flea can jump vertically up to 7 inches (18 cm) and horizontally up to 13 inches (33 cm), making the flea one of the best jumpers of all known animals (relative to body size), second only to the froghopper.
Bed bug bites cannot usually be identified by bites alone, as they look similar to mosquito and spider bites. Signs of a bed bug infestation include dark spots on bedding, eggs and eggshells (which are about 1mm across and white), and rusty or reddish stains on sheets caused by crushed bugs.
Check out the video below to learn about bed bug infestations:
Your pets are more likely to be bitten by fleas than you are. To see if a pet has fleas, part its hair or fur. Fleas will try to run and hide from the movement but will be visible. You can check more thoroughly using a special flea comb. Any fleas caught in the comb can be killed in soapy water.
Flea bites on humans show as clusters of red dots. While these bites can be anywhere on the body, they usually show up on the legs, ankles, and forearms, as exposure to fleas tends to come from being around or petting animals that are infested.
When not feeding, bed bugs can be found near the piping, seams and tags of mattresses, and in cracks in the bed frame and headboard. In heavily infested rooms, they can also be found in chair seams, between cushions, in curtain folds, under loose wallpaper and in drawer joints.
The most common type of fleas can be found on pets and hiding in the carpet and in upholstery. Fleas rarely live on human hosts in the US, although they can bite them.
Bed bug bites (cimicosis) can cause itchiness, skin rashes and blisters. Scratching may lead to secondary infection. In addition, they can have damaging psychological effects. However, bed bugs are not known to be a vector for transmitting diseases.
In contrast, fleas transmit a variety of viral, bacterial and rickettsial diseases to humans and other animals. Flea bites are very itchy and annoying. Some people and animals suffer allergic reactions to flea saliva resulting in rashes. Flea bites generally result in the formation of a slightly raised, swollen itching spot with a single puncture point at the center (similar to a mosquito bite). The bites often appear in clusters or lines of two bites, and can remain itchy and inflamed for up to several weeks afterwards. Fleas can also lead to hair loss as a result of frequent scratching and biting by the animal, and can cause anemia in extreme cases.
Bed bugs are notoriously difficult to kill or get rid of. The EPA suggest integrated pest management (IPM), which uses both chemical and non-chemical treatments. Suggested treatments include putting bedding and clothing in a dryer at high temperatures (as general washing will not kill bedbugs). Infested areas should be heated to at least 113F for an hour. Pesticides designed for indoor use on bedbugs can also be used. It is estimated that an average American family spends roughly $5,000 for bedbug treatment. Folk remedies include bean leaves.[1][2]
Flea infestations can be treated by vacuuming carpets, furnishings, cracks in floors and upholstery, plus any place pets sleep, to remove fleas and eggs. Rugs and pet bedding should be beaten outdoors. Fleas on pets should be killed using specially designed products on their fur.
Flea infestations can potentially be prevented by washing pet bedding every week. But bed bug infestations can be difficult to prevent. You should check secondhand furniture careful for signs of infestation and can eliminate hiding spots by using protective covers to encase mattresses and box springs. In hotel rooms, use luggage racks to hold luggage, and unpack directly into the washing machine when you return home.
In December 2014, researchers at Simon Fraser University announced that they had developed a chemical that attracted bed bugs from wherever they are in a room, thereby allowing them to be counted and killed. It is expected that this invention will be commercialized by late 2015, and will help prevent and even treat minor infestations. However, it may not work in heavily infested areas because female bed bugs tend to disperse rather than congregate when there is a large number of bed bugs around.
See the original post:
Bed Bugs vs Fleas - Difference and Comparison | Diffen

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location