Red welts cover your skin, and youve seen little red-brown bugs crawling on the mattress, but are you sure its bed bugs? Bed bugs can be mistaken for many other insects.
You need to know what pest youre dealing with to develop your action plan. The last thing you want to do is pay for an expensive treatment that doesnt target the nuisance pest.
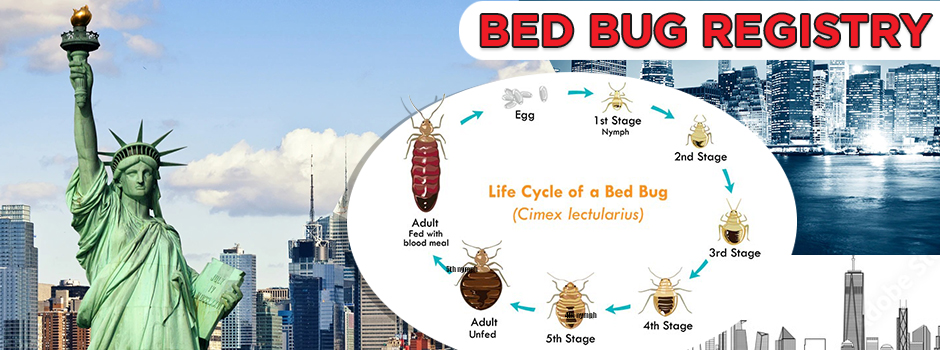
First, lets review what bed bugs look like:
Bed bug nymphs are smaller than adults and are whitish-yellow. When full of blood, they look bright or dark red. Without any blood, their bodies are translucent and almost invisible.
Bed bugs are the size of a poppy seed when they hatch from eggs. Bed bug eggs are about the size of a pinhead and are pearl-white.
Now lets take a closer look at 9 common insects that are often mistaken for bed bugs:
Baby cockroaches (cockroach nymphs) are often confused with bed bugs because of their similar coloring.
These young varieties of the most common cockroaches include German cockroaches, American cockroaches, brown-banded cockroaches, and Oriental cockroaches. Cockroaches have a flattened, oval appearance, long antenna, and long bristly legs.
Depending on the species, color ranges from reddish-brown to dark brown and from tan to black. Because theyre nymphs, they havent grown their cockroach wings, which also leads people to confuse them with bed bugs.
Where cockroach nymphs hide: Cockroaches thrive in moist areas where food is prepared or stored. Prime breeding grounds include restaurants, grocery stores, commercial kitchens, sewers, and steam tunnels. You may even see cockroaches hiding in your crawl space, bathroom, or basement.
Cockroach nymphs in your home may be a sign of an infestation.
Health risk: Because bacteria sticks to a cockroachs body, cockroaches may spread illnesses to people, such as salmonella and gastroenteritis. People allergic to cockroaches may experience asthma attacks, according to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America.
Booklice, which range in color from translucent white to gray or brown, are easily mistaken for adult bed bugs and baby bed bugs.
Where booklice hide: Booklice enjoy a moldy meal from the paste of old book bindings and wallpaper. If booklice are in your stored pantry items, this may be a sign mold is growing on your food.
Health risk: These bugs are a nuisance, but pose no threat. Their damage is typically minor.
Fun fact about booklice: Booklice, also called psocids, are not actual lice. Although they resemble lice in appearance, these little bugs feed on mold and fungi rather than blood.
Adult carpet beetle varieties vary in length, are oval-shaped, and can appear to be bed bug look-alikes. There are many species of carpet beetles, including the black, common, furniture, and varied carpet beetle.
These small pests feast on your animal origin materials, including furs, wools, feathers, or leather. Despite their name, theyre not fans of eating the synthetic materials of todays carpet. Theyll make an exception, though, if your carpet has a blend of synthetic materials, animal fabrics, food, sweat, and oils.
Where carpet beetles hide: Youll usually find carpet beetles around the edges of rugs and carpets, underneath upholstered furniture, or underneath baseboards.
Health risk: Carpet beetle larvae dont pose much danger to you, but they can cause significant damage to your carpet or your favorite wool sweater. The damage usually appears in one ruined patch, rather than many scattered holes. Carpet beetles also leave behind molted shells.
Spider beetles may resemble a bed bug that has just feasted on blood.
What is a spider beetle? These bugs look like small spiders due to their long legs and large, rounded abdomens. The American spider beetle has a reddish-brown to black, shiny, globe-shaped abdomen and pale yellow legs, head, thorax, and antennae.
Where spider beetles hide: Spiders beetles may forage in grain mills, pantries, warehouses, and attics that contain bird, rodent, or bat droppings.
Health risk:These pests can bite, and they may infest your foods.
Like bed bugs, bat bugs have an oval body and a short, broad head attached to the prothorax. The main difference between these two look-alikes is that bat bugs have longer (and more) hairs on their thorax.
Where bat bugs hide: Bat bugs develop in colonies of roosting bats, most often occurring in attics, behind walls, or in chimneys. When bats leave or are removed from the home, the remaining bat bugs may move into your living space and hide in dark crevices and fabric folds, including your mattress.
Health risk: Bat bugs primarily suck the blood of bats and will only bite humans if their bat host is unavailable. Although bat bugs are not known to transmit any diseases to people, their presence can cause anxiety and insomnia in some people.
Ticks are blood-sucking parasites, like bed bugs, and they can resemble each other until you look closely. The key difference? The number of their legs. Bed bugs, which are insects, have six legs; and ticks, which are arachnids, have eight.
Ticks attach to humans, pets, livestock, and wild animals. There are many types of ticks, each with different physical traits. Most ticks are small, dark in color, and flat when unfed.
Where ticks hide: Ticks are most commonly found attached to their host or outdoors in moist, shady areas with tall grass or overgrown vegetation. Occasionally a tick may be found indoors after being brought inside. Tick infestations indoors are rare, but they can occur if a female tick lays her eggs in your home.
Health risk: Ticks can pass many pathogens, like Lyme disease, to people, pets, and other animals. If these diseases are left untreated, many can become life-threatening. Its essential to know how to identify a tick dentify and how to remove a tick.
Fleas can be another bed bug impostor. Fleas can move quickly through fur, woven fabrics, and hair due to their narrow bodies, spiny legs, and backward-pointing bristles. Their hind legs make them excellent jumpers. These blood-suckers feed on cats, dogs, mice, birds, people, and many other warm-blooded animals.
Where fleas hide: Dogs and cats offer a feast for fleas, and pets are the chief way fleas get inside homes. Look for flea larvae in floor cracks, carpets, mattresses, or pet beds. Fleas especially like places where they can feed on food, animal waste, and adult flea feces.
Health risk: Though rare, fleas are capable of passing diseases (including typhus and plague) to people. Some people and pets may also experience severe allergic reactions to a fleas saliva. Your pet may experience anemia due to blood loss.
Is it a bed bug or lice? These two pests often are mistaken for each other.
Lice are host specific, so lice infesting dogs cant migrate to you, and you cant transmit this pest to your dog.
Head lice only affect people and are typically gray but can take on their hosts hair color. The female is about 1/16 to 1/8-inch long and flat in shape while the male is a bit smaller. Head lice cannot jump or fly.
If you have head lice and dont get treatment, the lice will continue to feed on your blood and may excrete dark red feces onto your scalp.
Where head lice hide: Head lice typically gather near the lower back of the head and behind the ears.
Health risk: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), head lice may cause severe itchiness in the scalp and lack of sleep. Excessive scratching may increase your chance of developing a secondary skin infection. Knowing safe and effective ways to remove lice can help you manage these risks.
Mites and bed bugs can look similar to some people.
There are thousands of mite species, many of which live on animals. Mites are tiny, and many can be seen with the naked eye. They measure 2 mm (or less) in length, have eight legs, and have little to no segmentation.
Where mites hide: Mites have a free-range lifestyle. Some feed on decaying organic matter, while others forage on insects and other mites. Some mite species inhabit their hosts ear canals, lungs, intestine, and bladder, particularly in domestic animals.
Health risk: According to the World Health Organization, some mites are vectors of rickettsial diseases, such as typhus fever, and several viral diseases. Certain mites cause scabies, a contagious, intensely itchy skin condition in which tiny mites burrow into the skin.
Although bed bugs have many doppelgngers, some signs may point to a bed bug infestation.
For starters, where did you find the suspected bed bug? Not all bed bug look-alikes are going to be hiding in the mattress, so where you find the bug can help you with identification.
If you found the bug in the bed, then odds are higher that you may have bed bugs. Is your head itchy? Then youre probably not dealing with bed bugs.
Keep in mind that bed bug bites are not enough to determine a bed bug infestation, as their bites look similar to flea bites and mosquito bites.
Conduct your own investigation. What pest in the bug lineup of photos above is the best match? If it looks like the cockroach nymph, you dont have a bed bug problem but may have a different pest problem to solve.
Bed bug removal is costly, so be sure you are dealing with a bed bug and not a cockroach or other pest control problem. Knowing ways to prevent bed bugs and how to check for bed bugsare essential to managing bed bugs.
When your bug investigation hits a dead end and youre stuck identifying the bug you found, call an expert.
A pest control professional near you can help identify the bug that caused your welts, draft a treatment plan and close the case of the mysterious bug you found in your home.
Main Photo Credit: Red spider mites /Aleksey Gnilenkov /CC BY 2.0
More here:
10 Bugs that Look Like Bed Bugs and How to Tell the Difference

 Residence
Residence  Location
Location